无意中被问到代码执行效率的问题,那就总结一下检测代码执行效率的几种方式:
一、装饰器
在函数上加装饰器,来得到函数的执行时间。
def cst_time(func, *args, **kwargs):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time.time()
ret = func(*args, **kwargs)
end = time.time()
timestrap = end -start
print('function %s running time is %s'%(func.__name__,timestrap))
return ret
return wrapper
二、timeit模块
用timeit模块来计算代码执行时间:
python3 -m timeit -n 4 -r 5 -s "import binaryTree" "binaryTree" #其中binaryTree表示python脚本文件名
或
python3 -m timeit -n 4 -r 5 -s "import binaryTree" "binaryTree.functionname" #可以指定脚本中某个具体的函数
参数:
-m mod : run library module as a script (terminates option list)
执行结果:
4 loops, best of 5: 0.0792 usec per loop
这表示测试了4次,平均每次测试重复5次,最好的测试结果是0.0792秒。
如果不指定测试或重复次数,默认值为10次测试,每次重复5次。
三、Linux的time命令
time -p python3 multiTree.py
执行结果:
real 0.09 # 执行脚本的总时间
user 0.04 # 执行脚本消耗的CPU时间
sys 0.00 # 执行内核函数消耗的时间
# real - (user + sys)的时间差,就是消耗在I/O等待和执行其他任务消耗的时间。
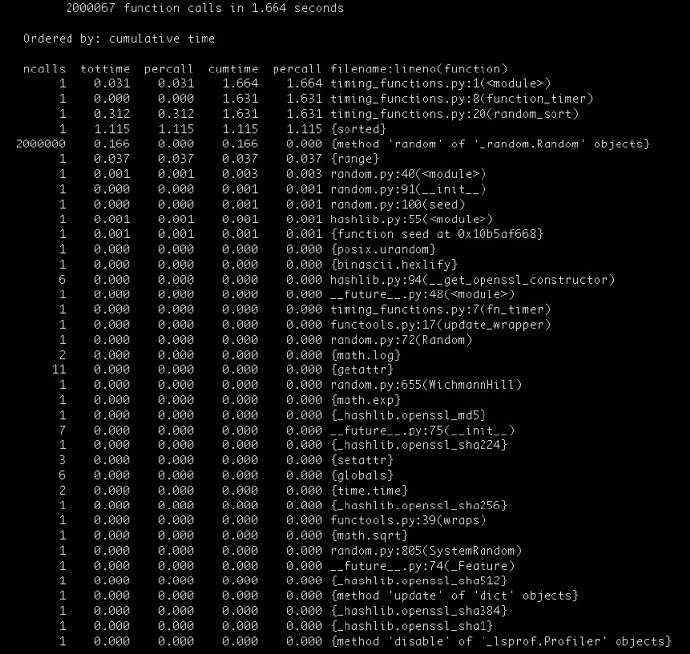
四、cProfile模块
如果想知道每个函数消耗的多少时间,以及每个函数执行了多少次,可以用CProfile模块。
python3 -m cProfile -s cumulative multiTree.py
执行结果:
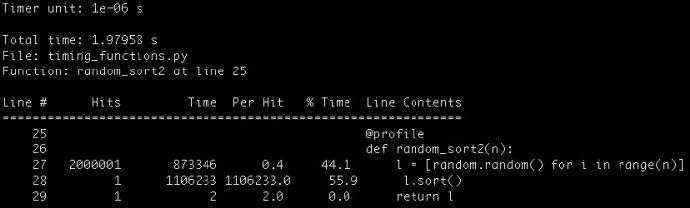
五、line_Profiler模块
使用line_Profiler可以给出执行每行代码所占用的CPU时间。
$ sudo pip3 install line_Profiler
用@profile 指定去检测那个函数,不需要导入模块。
@profile
def random_sort2(n):
l = [random.random() for i in range(n)]
l.sort()
return l
if __name__ == "__main__":
random_sort2(2000000)
可以通过如下命令逐行扫描每行代码的执行情况:
$ kernprof -l -v timing_functions.py
其中-l表示逐行解释,-v表示表示输出详细结果。通过这种方法,我们看到构建数组消耗了44%的计算时间,而sort()方法消耗了剩余的56%的时间。
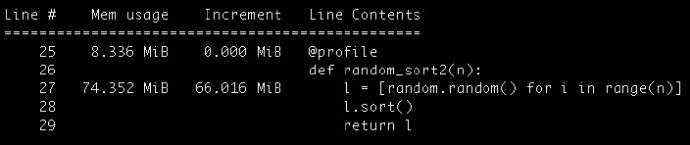
六、memory_profiler模块
逐行检测每行代码内存的使用的情况。但使用这个模块会让代码运行更慢。
$ sudo pip3 install memory_profiler
安装 psutil模块,会让memory_profiler运行更快。
$ sudo pip3 install psutil
在函数上加 @profile 装饰器来指定需要追踪的函数。
执行如下命令,查看结果:
$ python3 -m memory_profiler timing_functions.py
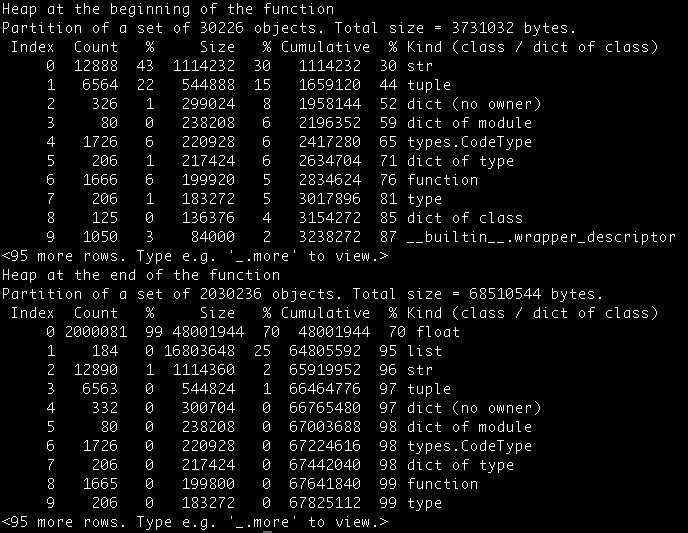
七、guppy模块
通过这个包可以知道在代码执行的每个阶段中,每种类型(str、tuple、dict等)分别创建了多少对象。
$ pip3 install guppy
将其添加到代码中:
from guppy import hpy
def random_sort3(n):
hp = hpy()
print( "Heap at the beginning of the functionn", hp.heap())
l = [random.random() for i in range(n)]
l.sort()
print( "Heap at the end of the functionn", hp.heap())
return l
if __name__ == "__main__":
random_sort3(2000000)
执行命令:
$ python3 timing_functions.py
查看结果:
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------