概念
PriorityQueue是一种支持排序的优先级队列,你入队列的对象需要实现Comparable或Comparator接口,或者它本身支持自然排序,如Integer,Long这些类型(这些类型也都实现了Comparable接口)。
数据结构
优先级队列底层的数据结构其实是一颗二叉堆,什么是二叉堆呢?我们来看看下面的图(a为大顶堆,b为小顶堆)
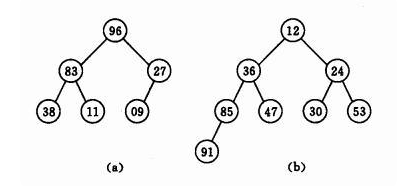
- 在这里我们会发现以下特征:
- 二叉堆是一个完全二叉树
- 根节点总是大于左右子节点(大顶堆),或者是小于左右子节点(小顶堆)。
java代码例子
- 定义一个对象,实现Comparable接口
@Data
static class Customer implements Comparable {
private int id;
private String name;
public Customer(int i, String n) {
this.id = i;
this.name = n;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Customer o) {
if (this.id
- 添加测试用例
@Test
public void test() {
Queue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(1, "zhansan"));
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(2, "lisi"));
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(4, "wangwu"));
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Customer cust = priorityQueue.poll();
System.out.println("Processing Customer =" + cust.toString());
}
}
- 测试结果,按着id的升序出队列
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=1, name=zhansan)
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=2, name=lisi)
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=4, name=wangwu)
@Data
static class Customer implements Comparable {
private int id;
private String name;
public Customer(int i, String n) {
this.id = i;
this.name = n;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Customer o) {
if (this.id @Test
public void test() {
Queue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(1, "zhansan"));
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(2, "lisi"));
priorityQueue.add(new Customer(4, "wangwu"));
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
Customer cust = priorityQueue.poll();
System.out.println("Processing Customer =" + cust.toString());
}
}
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=1, name=zhansan)
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=2, name=lisi)
Processing Customer =PriorityQueueTest.Customer(id=4, name=wangwu)











 京公网安备 11010802041100号
京公网安备 11010802041100号