SQL语句基本大同小异,只是记录下不同点
SQL Server一
constraint
可使用如下语句,表示当前操作的是Test数据库,当然也可以自己在SSMS中选择操作的数据库
use [Test]
go
1.添加主外键约束
可参考Creating and Working with tables - Part 3
语法为:
Alter table ForeignKeyTable add constraint ForeignKeyTable_ForiegnKeyColumn_FK
FOREIGN KEY (ForiegnKeyColumn) references PrimaryKeyTable (PrimaryKeyColumn)
2.添加默认约束
语法:
a.给现有的某列添加默认约束
ALTER TABLE { TABLE_NAME }
ADD CONSTRAINT { CONSTRAINT_NAME }
DEFAULT { DEFAULT_VALUE } FOR { EXISTING_COLUMN_NAME }
b.添加新的column,并添加默认约束
ALTER TABLE { TABLE_NAME }
ADD { COLUMN_NAME } { DATA_TYPE } { NULL | NOT NULL }
CONSTRAINT { CONSTRAINT_NAME } DEFAULT { DEFAULT_VALUE }
c.去掉约束
ALTER TABLE { TABLE_NAME }
DROP CONSTRAINT { CONSTRAINT_NAME }
3.级联引用完整性约束(Cascading referential integrity constraint)
如下,有主外键关联的表
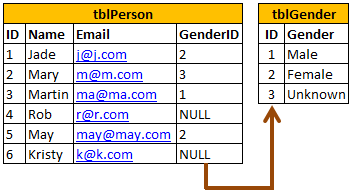
当删除tblGender表中ID为2的行时:
delete from tblGender where ID = 2
会提示如下的错误:
DELETE 语句与 REFERENCE 约束"tblPerson_GenderID_FK"冲突。该冲突发生于数据库"Test",表"dbo.tblPerson", column 'GenderID'。
可参考:
- Cascading referential integrity constraint - Part 5
- 级联引用完整性约束
有如下的值:
NO ACTION产生错误并回滚CASCADE删除或者更新所有包含那些外键的行SET NULL外键的所有值将被设置为 NULLSET DEFAULT设置为默认值
4.check约束
check约束用来限制value的范围,例如假设有Age列,Age不小于0也不能大于150
参考Check constraint in SQL Server - Part 6
ALTER TABLE tblPerson
ADD CONSTRAINT CK_tblPerson_Age CHECK (Age > 0 AND Age <150)
5.identity colunm
参考Identity column in SQL Server - Part 7
如果某个column被指定为identity colunm&#xff0c;那么当插入数据的时候这列的值就会自动生成
Create Table tblPerson
(
PersonId int Identity(1,1) Primary Key,
Name nvarchar(20)
)
也可以在SSMS中指定&#xff0c;如下&#xff1a;

如果要给identity colunm指定一个明确的值&#xff0c;如下&#xff1a;
a.首先打开Identity_Insert SET Identity_Insert tblPerson ON
b.插入值 Insert into tblPerson(PersonId, Name) values(2, &#39;John&#39;)
如果删除了表中所有的列&#xff0c;想重置identity colunm的值&#xff0c;使用DBCC CHECKIDENT命令
DBCC CHECKIDENT(tblPerson, RESEED, 0)
6.获取最后生成的identity列的值
参考How to get the last generated identity column value in SQL Server - Part 8
可使用&#xff1a;SCOPE_IDENTITY()和 &#64;&#64;IDENTITY、IDENT_CURRENT(&#39;TableName&#39;)
它们之间的区别&#xff1a;
SCOPE_IDENTITY() - returns the last identity value that is created in the same session and in the same scope.
&#64;&#64;IDENTITY - returns the last identity value that is created in the same session and across any scope.
IDENT_CURRENT(&#39;TableName&#39;) - returns the last identity value that is created for a specific table across any session and any scope.
7.Unique约束
参考Unique key constraint - Part 9
添加Unique约束
alter table tblPerson
add constraint Unique_Email Unique(Email)
主键约束和Unique约束的区别&#xff1f;
1.一个表只能有一个主键&#xff0c;但是可有多个unique key
2.主键不允许有null值&#xff0c;而unique key允许有null
select
1.SELECT DISTINCT
在表中&#xff0c;可能会包含重复值。关键词 DISTINCT 用于返回唯一不同的值。
如列出说有的City
select distinct City from tblPerson
注意select distinct Name, City from tblPerson表示的是去掉的是两列都相同的后的结果&#xff0c;其结果可能如下&#xff1a;
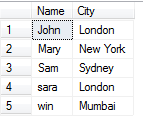
操作符和通配符
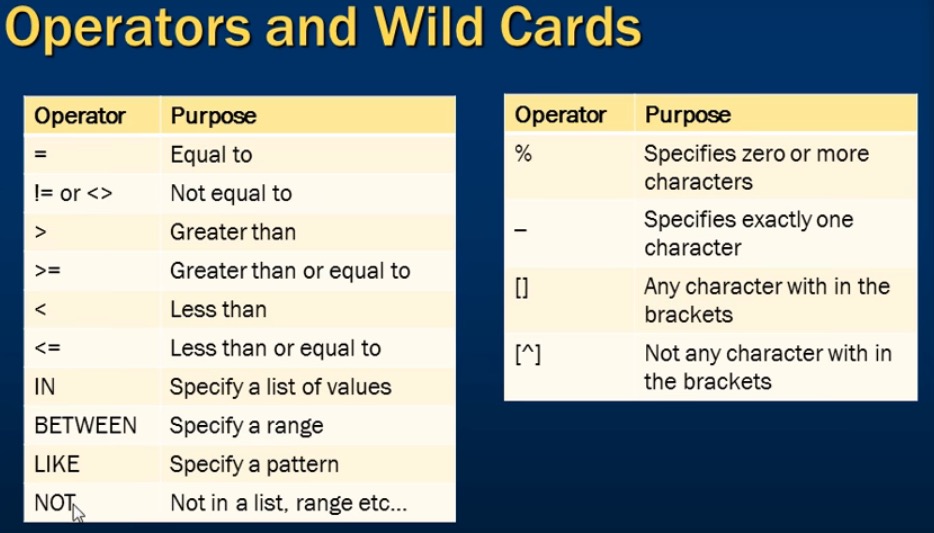
例如&#xff0c;选择Name以MST其中一个开头的行
select * from tblPerson where Name like &#39;[MST]%&#39;
top关键字&#xff0c;选择前多上行数据&#xff1a;
select top 5 * from tblPerson
也可以指定百分比&#xff0c;如下
select top 50 percent * from tblPerson
2.Group By
参考Group By - Part 11
聚合函数&#xff1a;Count() Sum() avg() Min() Max()
Group By总是和一个或多个聚合函数一起使用
如下的表tblPerson02
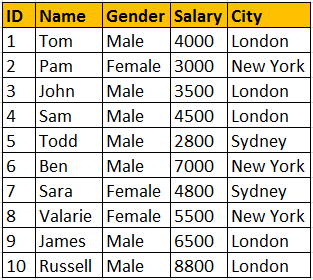
如果要按city来统计每个city要付的salary&#xff1a;
select city, sum(salary) as totalSalary from tblPerson02 group by city
如果要按按city、gender来统计每个city要付的salary&#xff0c;并统计数量&#xff1a;
select city, gender, sum(salary) as totalSalary, count(ID) as totalEmployees
from tblPerson02
group by city, gender
结果为&#xff1a;

HAVING子句用于过滤聚合之后的group。Where子句在聚合之前过滤行&#xff0c;而HAVING在聚合后&#xff0c;过滤group
如使用where子句&#xff1a;
Select City, SUM(Salary) as TotalSalary
from tblEmployee
Where City &#61; &#39;London&#39;
group by City
如使用having子句&#xff1a;
Select City, SUM(Salary) as TotalSalary
from tblEmployee
group by City
Having City &#61; &#39;London&#39;
Where和Having子句之间的区别&#xff1a;
1.where子句可用在select、insert、update语句中。而having子句只能用在select语句中
2.where子句在聚合&#xff08;Grouping&#xff09;之前过滤行&#xff0c;而having在聚合执行之后过滤group
3.聚合函数不能用在where子句中&#xff0c;除非包含在having子句中的子查询中。而having子句中可以使用聚合函数
如&#96;select * from tblPerson02 where sum(salary) > 4000&#96;&#xff0c;则会提示&#96;聚合不应出现在 WHERE 子句中&#xff0c;除非该聚合位于 HAVING 子句或选择列表所包含的子查询中&#xff0c;并且要对其进行聚合的列是外部引用&#96;。
而如下可正常执行
select city, gender, sum(salary) as totalSalary, count(ID) as totalEmployees
from tblPerson02
group by city, gender
having sum(salary) > 5000
join
参考Joins in sql server - Part 12
SQL Server中&#xff0c;join的类型&#xff1a;
- CROSS JOIN 笛卡尔积
- INNER JOIN 等同于join
OUTER JOIN 分为三种&#xff1a;
- Left Join or Left Outer Join
- Right Join or Right Outer Join
- Full Join or Full Outer Join
不同join之间的区别&#xff1a;
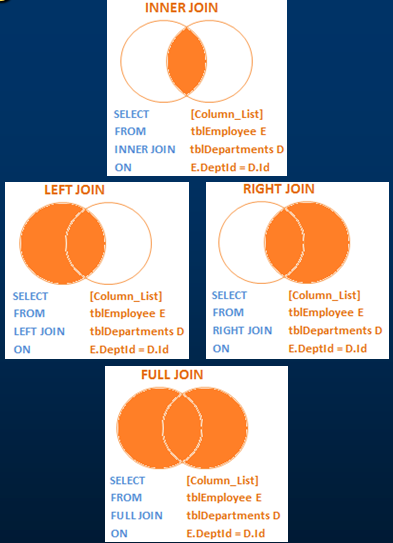
Advanced Joins
参考Advanced Joins - Part 13
如下的两张表tblEmployee和tblDepartment
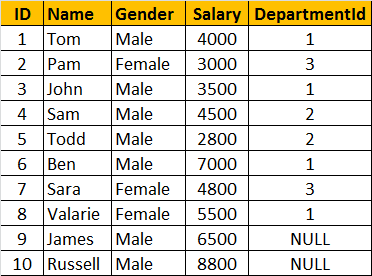
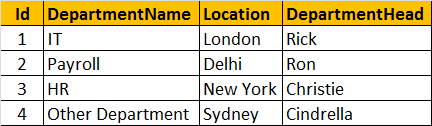
1.只获取左表中不匹配的数据

SELECT Name, Gender, Salary, DepartmentName
FROM tblEmployee E
LEFT JOIN tblDepartment D
ON E.DepartmentId &#61; D.Id
WHERE D.Id IS NULL
2.只获取右表中不匹配的数据
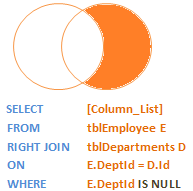
SELECT Name, Gender, Salary, DepartmentName
FROM tblEmployee E
RIGHT JOIN tblDepartment D
ON E.DepartmentId &#61; D.Id
WHERE E.DepartmentId IS NULL
3.获取左右表中都不匹配的数据

SELECT Name, Gender, Salary, DepartmentName
FROM tblEmployee E
FULL JOIN tblDepartment D
ON E.DepartmentId &#61; D.Id
WHERE E.DepartmentId IS NULL
OR D.Id IS NULL
自连接
参考Self join in sql server - Part 14
SQL Server中替换NULL的不同方式
参考Different ways to replace NULL in sql server - Part 15
1.使用ISNULL()函数
2.使用CASE 语句
3.使用COALESCE()函数
UNION与UNION ALL
参考Union and union all in sql server - Part 17
UNION与UNION ALL的区别在于&#xff0c;UNION移除重复的行&#xff0c;UNION ALL并不移除重复的行
UNION与JOIN的区别
JOINS and UNIONS are different things. However, this question is being asked very frequently now. UNION combines the result-set of two or more select queries into a single result-set which includes all the rows from all the queries in the union, where as JOINS, retrieve data from two or more tables based on logical relationships between the tables. In short, UNION combines rows from 2 or more tables, where JOINS combine columns from 2 or more table.
存储过程
参考Stored procedures - Part 18
存储过程是一组T-SQ语句
1.创建不带参数的存储过程
如下&#xff0c;获取从tblEmployee中获取所有的Name和Gender
create procedure spGetEmployees
as
beginselect Name, Gender from tblEmployee
end
注意&#xff1a;在命名存储过程时&#xff0c;Microsoft建议不要使用“sp_”作为前缀&#xff0c;所以系统的存储过程&#xff0c;使用“sp_”作为前缀
执行以上的存储过程&#xff0c;可以有如下的形式&#xff1a;
spGetEmployeesEXEC spGetEmployeesExecute spGetEmployees
也可以右键存储过程名字&#xff0c;选择 EXECUTE STORED PROCEDURE
2.带输入参数的存储过程
参数和变量前有&#64;前缀
Create Procedure spGetEmployeesByGenderAndDepartment
&#64;Gender nvarchar(50),
&#64;DepartmentId int
as
BeginSelect Name, Gender from tblEmployee Where Gender &#61; &#64;Gender and DepartmentId &#61; &#64;DepartmentId
End
执行这个存储过程&#xff0c;需要传递参数&#xff0c;注意参数的顺序
EXECUTE spGetEmployeesByGenderAndDepartment &#39;Male&#39;, 1
如果指定了参数的名字&#xff0c;可以不在意顺序
EXECUTE spGetEmployeesByGenderAndDepartment &#64;DepartmentId&#61;1, &#64;Gender &#61; &#39;Male&#39;
3.带输出参数的存储过程
参考Stored procedures with output parameters - Part 19
要使用关键字OUT或者OUTPUT
Create Procedure spGetEmployeeCountByGender
&#64;Gender nvarchar(20),
&#64;EmployeeCount int Output
as
BeginSelect &#64;EmployeeCount &#61; COUNT(Id) from tblEmployee where Gender &#61; &#64;Gender
End
执行带有输出参数的存储过程
1.初始化一个同样数据类型的输出参数
2.把变量传递到存储过程&#xff0c;要指定OUTPUT关键字&#xff0c;如果没有指定OUTPUT关键字&#xff0c;变量就为NULL
3.执行
Declare &#64;EmployeeTotal int
Execute spGetEmployeeCountByGender &#39;Female&#39;, &#64;EmployeeTotal output
Print &#64;EmployeeTotal
如果使用变量的名字&#xff0c;可以在任意位置传递参数
Declare &#64;EmployeeTotal int
Execute spGetEmployeeCountByGender &#64;EmployeeCount &#61; &#64;EmployeeTotal OUT, &#64;Gender &#61; &#39;Male&#39;
Print &#64;EmployeeTotal
一些非常有用的系统的存储过程
1.sp_help SP_Name 显示存储过程的信息
2.sp_helptext SP_Name显示存储过程的text
3.sp_depends SP_Name显示存储过程的依赖