作者:隆威SU_486 | 来源:互联网 | 2024-09-28 19:47
本篇内容主要讲解“如何理解MyBatis动态SQL”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“如何理解MyBatis动态SQL”吧!
目录
前言
动态sql
1.先看一下模块目录结构
2.物理建模和逻辑建模
3. 引入依赖
4.全局配置文件
5.sql共性抽取文件
6.mapper接口
if
where
用if标签的动态sql:
where和if的动态sql:
trim
set
trim的动态sql:
set的动态sql
set标签的作用:
choose、when、otherwise
foreach
1.动态sql
2.动态sql
批量查询:foreach标签
测试程序
前言
前面mysql都是通过静态sql进行查询的,但是如果业务复杂的时候,我们会遇到引号问题,或者多一个空格,这就使得sql代码编写错误了,所以为了解决这个问题,我们有了动态sql。
Mybatis框架的动态SQL技术是一种根据特定条件动态拼装SQL语句的功能,它存在的意义是为了解决拼接SQL语句字符串时的痛点问题。具体是通过标签来实现的。
动态sql
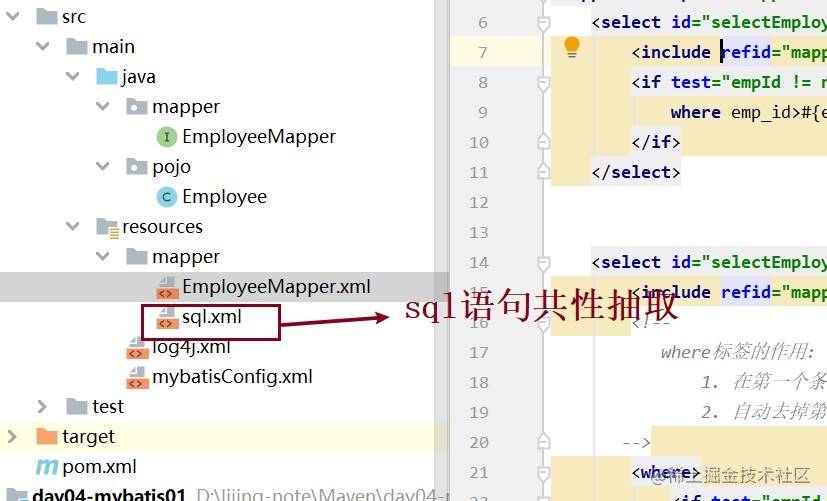
1.先看一下模块目录结构
在类路径的resources下的mapper包下创建sql.xml文件(共性抽取)
2.物理建模和逻辑建模
这里省略物理建模步骤,要求数据库的表与pojo类要对应。
package pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private Integer empId;
private String empName;
private Double empSalary;
}3. 引入依赖
把之前的log4j复制到类路径resouces下,另外我们引入依赖后的pom.xml如下:
4.0.0
org.example
day03-mybatis02-dynamic
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.18.8
provided
org.mybatis
mybatis
3.5.7
junit
junit
4.12
test
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.3
runtime
log4j
log4j
1.2.17
4.全局配置文件
注意: 这里有驼峰映射,别名映射,路径映射和路径映射。和以前的不同的是,我们这里做了sql语句的共性抽取,所以得加一个sql的路径映射
5.sql共性抽取文件
在类路径resources下的包mapper下创建一个sql.xml(因为我们sql是要写在映射文件中,自己本身也是映射文件,所以需要写在mapper下)。到要用的时候,在映射路径文件中需要用到这个sql语句的地方加入 。
select emp_id,emp_name,emp_salary from t_emp
共性抽取文件也可以不配置,这时候直接在映射文件中把要执行的语句重新编写就行了。
6.mapper接口
一共有七个方法
package mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import pojo.Employee;
import java.util.List;
public interface EmployeeMapper {
//根据员工的empId查询大于该empId的所有员工,如果empId为null,则查询全体员工
List selectEmployeeListByEmpId(Integer empId);
/**
* 查询大于传入的empId并且工资大于传入的empSalary的员工集合,如果传入的empId为null,则不考虑empId条件
* 传入的empSalary为null则不考虑empSalary的条件
*/
List selectEmployeeListByEmpIdAndEmpSalary(@Param("empId") Integer empId, @Param("empSalary") Double empSalary);
/**
* 根据empId更新员工信息,如果某个值为null,则不更新这个字段
*/
void updateEmployee(Employee employee);
/**
* 根据emp_id查询员工信息,如果0 selectEmployeeList(Integer empId);
/**
* 添加员工信息
*/
void insertEmployee(Employee employee);
/**
* 批量添加员工集合
*/
void insertEmployeeList(@Param("employeeList") List employeeList);
/**
* 根据员工的id集合查询员工集
*/
List selectEmployeeListByEmpIdList(List idList);
}if
目标:根据员工的empId查询大于该empId的所有员工,如果empId为null,则查询全体员工。
Dao接口的方法为:
List selectEmployeeListByEmpId(Integer empId);
静态sql:
where emp_id>#{empId}
动态sql:
where emp_id>#{empId}
where
目标:
查询大于传入的empId并且工资大于传入的empSalary的员工集合
如果传入的empId为null,则不考虑empId条件
传入的empSalary为null则不考虑empSalary的条件
Dao接口方法:
List selectEmployeeListByEmpIdAndEmpSalary(@Param("empId") Integer empId, @Param("empSalary") Double empSalary);
用if标签的动态sql:
where
emp_id>#{empId}
and emp_salary>#{empSalary}
这里可以看到,如果empSalary为空,那么sql语句为select * from t_emp where emp_id >#{empId},但是如果empId为空,那么sql语句为select * from t_emp where and emp_salary>#{empSalary},很明显这个是错的,if标签在这里就不适用了。所以我们用where标签,或者trim标签。
where和if的动态sql:
emp_id>#{empId}
and emp_salary>#{empSalary}
where标签的作用:
在第一个条件之前自动添加WHERE关键字
自动去掉第一个条件前的连接符(AND、OR等等)
trim
trim是修建的意思,其实就是去头去尾,这里还是根据上面那个方法
trim的动态sql
emp_id>#{empId}
AND emp_salary>#{empSalary}
trim标签:
set
目标:根据empId更新员工信息,如果某个值为null,则不更新这个字段
Dao接口方法:
void updateEmployee(Employee employee);
我们先用上面的trim标签来解决一下这个问题,
trim的动态sql:
emp_name=#{empName}
, emp_salary=#{empSalary}
where emp_id=#{empId}
set的动态sql
update t_emp
emp_name=#{empName}
, emp_salary=#{empSalary}
可以看出
set标签的作用:
自动在要修改的第一个字段之前添加SET关键字
去掉要修改的第一个字段前的连接符(,)
choose、when、otherwise
目标:
Dao接口方法:
List selectEmployeeList(Integer empId);
动态sql
where
0 and empId<6">
emp_id>#{empId}
6">
emp_id<#{empId}
1==1
choose、when、otherwise
相当于if ... else if... else if ... else
foreach
目标1:批量添加员工信息
Dao接口方法:
void insertEmployeeList(@Param("employeeList") List employeeList);
1.动态sql
insert into t_emp(emp_name,emp_salary)values
(#{emp.empName},#{emp.empSalary})
目标2:根据多个id查询多个员工信息
Dao接口
List selectEmployeeListByEmpIdList(List idList);
2.动态sql
#{id}
批量查询:foreach标签
collection属性: 表示要遍历的对象,如果要遍历的参数使用@Param注解取名了就使用该名字,如果没有取名List,或者collection。
item属性: 表示遍历出来的元素,我们到时候要拼接SQL语句就得使用这个元素: 如果遍历出来的元素是POJO对象, 那么我们就通过 #{遍历出来的元素.POJO的属性} 获取数据;如果遍历出来的元素是简单类型的数据,那么我们就使用 #{遍历出来的元素} 获取这个简单类型数据
separator属性: 遍历出来的元素之间的分隔符
open属性: 在遍历出来的第一个元素之前添加前缀
close属性: 在遍历出来的最后一个元素之后添加后缀
测试程序
import mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import pojo.Employee;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Test {
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
private InputStream is;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
@Before
public void init() throws Exception{
//目标:获取EmployeeMapper接口的代理对象,并且使用该对象调用selectEmployee(1)方法,然后返回Employee对象
//1. 将全局配置文件转成字节输入流
is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatisConfig.xml");
//2. 创建SqlSessionFactoryBuilder对象
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
//3. 使用构建者模式创建SqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
//4. 使用工厂模式创建一个SqlSession对象
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//5. 使用动态代理模式,创建EmployeeMapper接口的代理对象
employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
}
@After
public void after() throws Exception{
//提交事务!!!
sqlSession.commit();
//7. 关闭资源
is.close();
sqlSession.close();
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testSelectEmployeeListByEmpId(){
System.out.println(employeeMapper.selectEmployeeListByEmpId(null));
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testSelectEmployeeListByEmpIdAndEmpSalary(){
System.out.println(employeeMapper.selectEmployeeListByEmpIdAndEmpSalary(2, 300d));
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testUpdateEmployee(){
Employee employee = new Employee(3,"celia", 9000d);
employeeMapper.updateEmployee(employee);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testSelectEmployeeList(){
System.out.println(employeeMapper.selectEmployeeList(7));
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testInsertEmployee(){
employeeMapper.insertEmployee(new Employee(null,"tom",300d));
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testInsertEmployeeList(){
List employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 11; i <=20 ; i++) {
employeeList.add(new Employee(null,"aobama"+i,2000d));
}
employeeMapper.insertEmployeeList(employeeList);
}
@org.junit.Test
public void testSelectEmployeeListByEmpIdList(){
List idList = new ArrayList<>();
idList.add(23);
idList.add(33);
idList.add(32);
idList.add(21);
idList.add(22);
System.out.println(employeeMapper.selectEmployeeListByEmpIdList(idList));
}
}到此,相信大家对“如何理解MyBatis动态SQL”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是编程笔记网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!