作者:xts2011188_706_120_582 | 来源:互联网 | 2023-10-12 11:56
一、单链表基本知识
(一)动态链表(线性表)
-
每个元素实际上是一个单独的结构体对象,而所有对象都通过每个元素中的指针链接在一起
-
每个结构体对象叫做节点(包含数据域、指针域),节点是动态生成的(malloc)
-
第一个数据节点叫做链表的首元节点
-
第一个节点不用于存储数据,只用于代表链表的起始点,则这个节点称为链表的头节点
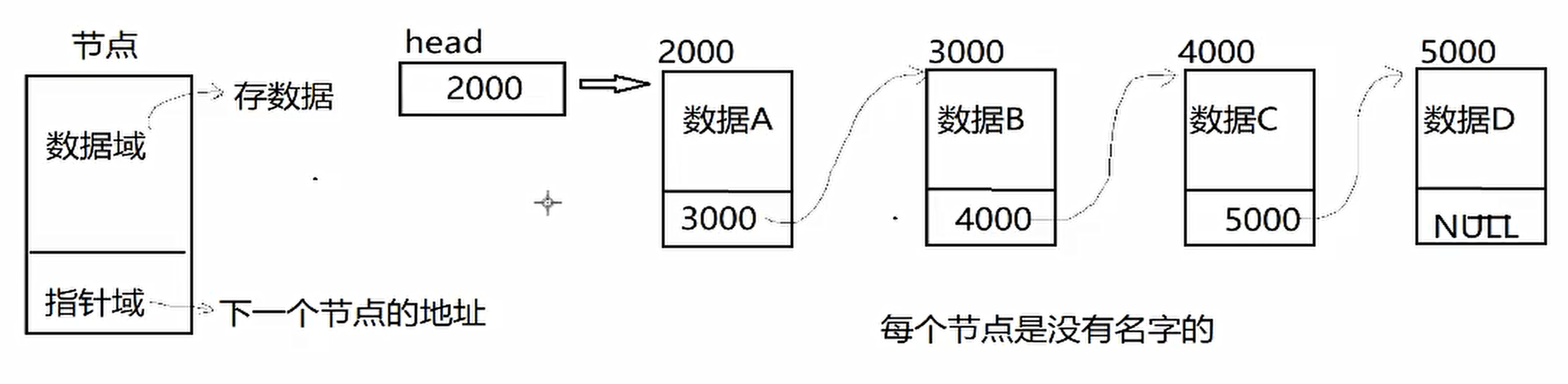
(二)特点
(三)区别
二、头文件
(一)防止头文件重复包含
#pragma once #ifndef LINKLIST#define LINKLIST#endif // 程序文件的最尾端
(二)一些简单的声明
typedef int Type; // 数据域的数据类型,通过取别名的方式灵活运用,一改全改#define TYPE_P "%d->" // 输入#define TYPE_S "%d" // 输出
(三)链表节点结构体的声明
-
数据域的类型:自定义,根据需要存储的数据类型
-
指针域的类型:与结构体类型相同
typedef struct Node{Type data; // 数据域:用于存储数据struct Node *next; // 指针域:用于指向下一个节点}Node;// 取别名Node可以省略定义变量struct Node
(四)整个链表结构体的声明
typedef struct LinkList{Node *head; // 整个链表的头节点指针Node *end; // 整个链表的尾节点指针int lenth;}LL; // 记录整个链表的头尾
(五)单链表功能的声明
LL *list_init(); // 1、单链表的创建Node *node_init(Type val); // 2、单链表节点的创建,val为需要存储的数据void list_insert_end(LL *list,Type val); // 3、单链表节点的插入,向单链表的尾部插入数据(尾插法)void list_insert(LL *list, int index, Type val); // 3、单链表节点的插入,向单链表指定位置插入数据,index为指定的位置void list_print(LL * list); // 4、单链表的输出Type list_delete_Node(LL *list, int index); // 5、单链表节点的删除,并返回被删除节点的数据,index为指定的位置Type list_get(LL *list, int index); // 6、获取单链表指定位置上的数据void list_delete_all(LL **list);// 7、单链表的销毁void stu_help(void); // 打印各功能说明
三、函数功能实现
(一)声明头文件
#include "LinkList.h" // 包含单链表头文件
(二)单链表的创建
LL *list_init(){// 动态创建一个单链表结构LL *temp = (LL*)malloc(sizeof(LL));// 如果动态内存开辟失败,temp指针指向NULLif (NULL == temp){ printf("单链表创建失败!\n");return NULL;}temp->head = NULL; // 链表头节点指针置空(初始化为空,防止野指针的出现)temp->end = NULL; // 链表尾节点指针置空(初始化为空,防止野指针的出现)temp->lenth = 0; // 链表长度初始化为0return temp;}
(三)节点的创建
Node *node_init(Type val) // val为需要存储的数据{// 创建一个新节点Node * temp = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));// 如果动态内存开辟失败,temp指针指向NULLif (NULL == temp){ printf("单链表节点创建失败!\n");return NULL;}temp->data = val; // 将新数据放入新节点中temp->next = NULL; // 节点指针域初始化为NULLreturn temp;}
(四)数据的插入
1、向单链表的尾部插入数据(尾插法)
void list_insert_end(LL *list, Type val)
{if (NULL == list){ // 如果整个链表不存在printf("链表空间不存在,插入数据失败!\n");return;}if (list->head == NULL){ // 如果链表为空,就创建第一个节点list->head = list->end = node_init(val);// 链表的第一个节点,既是链表头部,又是链表尾部list->lenth++; // 链表长度+1}else // 如果不是第一个节点的创建,需要将新节点连接上链表尾部{ // 新数据一定要放在新结点中list->end->next = node_init(val); // 创建新节点连接上当前链表尾部list->end = list->end->next; // 新节点成为新的尾部list->lenth++; //链表长度+1}
}
2、向单链表指定位置插入数据
void list_insert(LL *list, int index, Type val) // index为指定的位置
{if (NULL == list){ // 如果整个链表不存在printf("链表不存在,插入数据失败!\n");return;}if (index <= 0 || index > list->lenth + 1){printf("插入位置错误!\n");return;}// 在头节点之前插入if (index == 1){ // 如果插入位置是第一个Node * New = node_init(val); // 创建新节点New->next = list->head; // 新节点插入头节点之前(第一个位置)list->head = New; // 新节点成为新的头节点list->lenth++;return;}// 在尾节点之后插入if (index == list->lenth +1){ // 如果插入位置刚好比链表长度大一个(在链表尾部之后插入新数据) list_insert_end(list, val); // 调用尾插函数完成尾插return;}// 中间节点的插入Node * temp = list->head;for (int i = 1; i next;}Node * New = node_init(val); // 创建新节点New->next = temp->next; // 新节点连接上插入位置之后的节点temp->next = New; // 链表插入位置之前的节点连接上新节点list->lenth++; // 链表长度+1
}
(五)单链表的输出
void list_print(LL * list)
{if (NULL == list){ // 如果整个链表不存在printf("链表空间不存在,输出失败!\n");return; }if(NULL == list->head){printf("链表为空!\n") }for (Node * temp = list->head; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next){printf(TYPE_P, temp->data);}puts("NULL\n");
}
(六)单链表节点的删除,并返回被删除节点的数据
Type list_delete_Node(LL *list, int index) // index为指定的位置
{if (NULL == list){ // 如果整个链表不存在printf("链表不存在,删除数据失败!\n");return;}if (NULL == list->head){ printf("链表没有数据,删除数据失败!\n");return;}if (index <= 0 || index > list->lenth + 1){printf("删除位置错误!\n");return;}if (index == 1){ // 删除头部节点Node * temp = list->head; // 记录被删除的头节点list->head = list->head->next; // 头节点的下一个节点成为新的头部Type val = temp->data; // 记录被删除节点的数据free(temp);list->lenth--;return val;}if (index == list->lenth){ // 删除尾部节点Node *temp = list->head;for (int i = 1; i next;}Type value = temp->next->data; // 记录尾节点数据free(list->end); // 释放尾节点list->end = temp; // 尾节点的前一个节点(倒数第二个节点)成为新的尾部temp->next = NULL; // 新的尾部的next指针指向空list->lenth--;return value;}// 在中间删除Node * temp1 = list->head;for (int i = 1; i next;}Node *temp2 = temp1->next; // 记录被删除节点的位置Type val = temp2->data; // 记录被删除节点的数据temp1->next = temp2->next; // 删除位置的前一个节点的指针域跳过被删除位置的节点,指向下一个节点free(temp2); // 释放被删除节点的内存list->lenth--; // 单链表长度-1return val;
}
(七)获取单链表指定位置上的数据
Type list_get(LL *list, int index) // index为指定的位置
{if(list == NULL){printf("错误,单链表空间不存在!\n");return 0;}if(index > list_lenth || index <= 0){printf("位置错误!");return 0; }Node *temp = list->head;//找到需要查看的数据for (int i = 1; i next; }return temp->data;
}
(八)单链表的销毁
void list_delete_all(LL **list)
{if(*list == NULL){printf("错误,链表空间不存在!\n");return; }Node *temp1 = (*list)->head,*temp2;for(;temp1 != NULL;){temp2 = temp1;temp1 = temp1->next;free(temp2); }free(*list);*list = NULL;
}
四、主函数
(一)分文件编写
#include "LinkList.h" // 包含单链表头文件
(二)单链表功能的测试
void test()
{LL * LinkList1 = list_init(); // 单链表的初始化Type values; // 临时变量puts("请输入单链表的数据:");do{scanf(TYPE_S, &values);list_insert_end(LinkList1, values);} while (&#39;\n&#39; != getchar()); // 循环输入数据,以回车结束puts("当前单链表中的数据为:");list_print(LinkList1); // 单链表的输出list_insert(LinkList1, 3, 11); // 在第3个位置插入数据11puts("当前单链表中的数据为:");list_print(LinkList1); // 单链表的输出list_delete_Node(LinkList1, 5); // 删除第5个位置上的数据puts("当前单链表中的数据为:");list_print(LinkList1); // 单链表的输出
}int main()
{test();system("pause");return 0;
}