并发编程系列之ThreadLocal实现原理
ThreadLocal看词义,线程本地变量?线程的变量,要怎么定义?怎么使用?ThreadLocal是线程安全的?下面给出一个简单例子,引出本文
public class A {
void doSome1() {
int a = 11;
}
void doSome2() {
int a = 12;
}
void doSome3() {
doSome1();
doSome2();
}
}
public class A {
public static int count =1;
}
引用ThreadLocal里的代码注释:
This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., a user ID or Transaction ID).
ThreadLocal是一个线程的本地变量,可以理解为线程的变量,在线程执行过程随时可以访问。ThreadLocal变量,只有当前线程才能访问,其它线程不能访问,所以本质上ThreadLocal就是线程安全的。所以ThreadLocal的作用和上面例子说的局部变量一样是线程安全的。
前面的学习,我们知道要保证线程安全,一般就是想到加锁,不管是synchronized还是cas锁等,都会在并发的时候对性能产生一定的影响。ThreadLocal是怎么实现线程安全的?详细可以学习一下ThreadLocal源码
ThreadLocal主要的方法有:
// 获取当前线程本地变量的值
public T get() {}
// 给当前线程本地变量设置值
public void set(T value){}
// 清除当前线程本地变量的值。
public void remove(){}
// 统一初始化所有线程的ThreadLocal的值
public static ThreadLocal withInitial(Supplier supplier) {
}
主要变量:
// 调用nextHashCode()方法获取下一个hashCode值
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
// AmoicInteger原子类,用于计算hashCode值
private staitc AmoicInteger nextHashCode = new AmoicInteger();
// 斐波那契数,也叫黄金分割数,可以让hash值分布非常均匀
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
// 获取下一个hashCode值方法,只用原子类操作
private static int nextHashCode () {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
看了源码,找到set方法都可以找到一个关键的ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap 是 ThreadLocal 类的一个静态内部类
ThreadLocalMap is a customized hash map suitable only for maintaining thread local values.
ThreadLocal是ThreadLocal里自定义的hash map,当然和jdk里的HashMap实现是不同,这个map主要作用也是存储ThreadLocal变量值
ThreadLocalMap内部维护着一个Entry节点,Entry继承WeakReference,泛型是ThreadLocal,key申明为ThreadLocal k,实际上就是ThreadLocal的弱引用
/**
* The entries in this hash map extend WeakReference, using
* its main ref field as the key (which is always a
* ThreadLocal object). Note that null keys (i.e. entry.get()
* == null) mean that the key is no longer referenced, so the
* entry can be expunged from table. Such entries are referred to
* as "stale entries" in the code that follows.
*/
static class Entry extends WeakReference
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
| 引用类型 | 回收时间 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| 强引用 | JVM停止运行时 | 对象的一般状态 |
| 软引用 | 当内存不足时 | 对象缓存 |
| 弱引用 | 正常垃圾回收时 | 对象缓存 |
| 虚引用 | 正常垃圾回收时 | 跟踪对象的垃圾回收 |
Thread、ThreadLocalMap、ThreadLocal 结构关系图:
每一个Thread都有一个threadLocals变量,这个threadLocals变量其实就是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap,ThreadLocalMap被设计为ThreadLocal的内部类,在ThreadLocalMap内部类里,在其静态内部类Entry是以ThreadLocal的虚引用为key
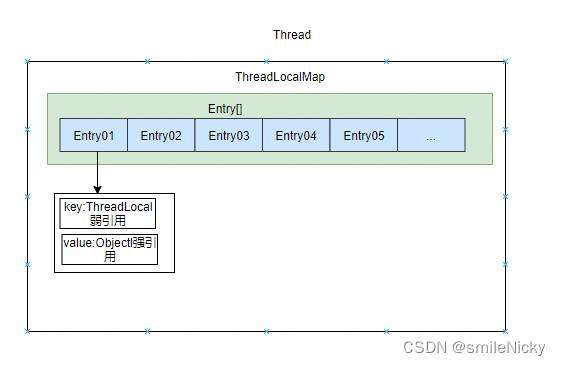
Thread、ThreadLocalMap、ThreadLocal 类关系图:

public void set(T value) {
// 获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
// map不为null,调用ThreadLocalMap的set方法设置值
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
// map为null,调用createMap方法初始化创建map
createMap(t, value);
}
// 获取当前线程的threadLocals,也就是ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
// 创建ThreadLocalMap
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
// ThreadLocalMap构造函数
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
// 初始化Entry表的容量默认为16
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
// 数组下标,hashCode与(INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1)
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
// 创建Entry
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
// size初始化为1
size = 1;
// 设置扩容阙值 ,默认为 len * 2 / 3
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
// 设置阙值
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
所以,set方法主要流程为:
ThreadLocalMapThreadLocalMap 的set方法设置值createMap方法创建ThreadLocalMap看起来并不复杂,其实并不然,复杂的逻辑在ThreadLocalMap的set方法里
private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) {
// 获取Entry表
Entry[] tab = table;
// 获取表长度
int len = tab.length;
// 获取数组下标 ,hashcode 与 (len-1)
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// 找到key相同的就更新value的值
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
// key为null,说明key过期了,被gc回收
if (k == null) {
// 初始化探测式清理的起始位置,替换过期元素
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
// 没有找到key相等的entry,而且没有key过期的entry,新建一个entry
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
// 存放元素数量+1
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
replaceStaleEntry方法:
private void replaceStaleEntry(ThreadLocal key, Object value,
int staleSlot) {
// 获取Entry表
Entry[] tab = table;
// Entry表长度
int len = tab.length;
Entry e;
// 定义探测式清理起始位置
int slotToExpunge = staleSlot;
// 从staleSlot开始遍历查找是否有key为null的,有就更新slaleSlot
for (int i = prevIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = prevIndex(i, len))
if (e.get() == null)
slotToExpunge = i;
// staleSlot开始向后循环
for (int i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// 如果找到key相同的entry,就替换staleSlot和i的位置,更新value的值
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
// 替换staleSlot和i的位置
tab[i] = tab[staleSlot];
// 更新value的值
tab[staleSlot] = e;
// 向前循环的没有查找到key过期的entry,更新slotToExpunge值
if (slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
// 会调用启动式过期清理,先会进行一遍过期元素探测操作
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
return;
}
// 没找到过期的key,更新slotToExpunge
if (k == null && slotToExpunge == staleSlot)
slotToExpunge = i;
}
// 找到Entry为null的数据,将数据放入该槽位
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = new Entry(key, value);
// 从staleSlot开始向前迭代查找有key=null的entry
if (slotToExpunge != staleSlot)
// 调用启动式过期清理,先会进行一次过期元素探测,如果发现了有过期的数据就会先进行探测式清理
cleanSomeSlots(expungeStaleEntry(slotToExpunge), len);
}
探测式清理:
private int expungeStaleEntry(int staleSlot) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 将起始位置置空
tab[staleSlot].value = null;
tab[staleSlot] = null;
// 元素数量减1
size--;
Entry e;
int i;
for (i = nextIndex(staleSlot, len);
(e = tab[i]) != null;
i = nextIndex(i, len)) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
// key为null,说明过期了,被GC回收
if (k == null) {
// 清空元素,并减1
e.value = null;
tab[i] = null;
size--;
} else {
// key没有过期,则重新计算hash,重新获取下标
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (len - 1);
if (h != i) {
// i位置槽置空
tab[i] = null;
// Unlike Knuth 6.4 Algorithm R, we must scan until
// null because multiple entries could have been stale.
// 寻找离冲突key所在entry最近的空槽,放入该槽
while (tab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, len);
tab[h] = e;
}
}
}
return i;
}
启动式清理:
private boolean cleanSomeSlots(int i, int n) {
boolean removed = false;
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
do {
// 从下一个位置开始
i = nextIndex(i, len);
Entry e = tab[i];
// 遍历到key==null的Entry
if (e != null && e.get() == null) {
// 重置n
n = len;
// 标志有清理元素
removed = true;
// 清理
i = expungeStaleEntry(i);
}
} while ( (n >>>= 1) != 0); // log(n) 限制 对数次
return removed;
}
public T get() {
// 获取当前线程
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
// map获取得到,返回value
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
// 未找到的话,则调用setInitialValue()方法设置null
return setInitialValue();
}
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
// key相等直接返回
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
// key不相等,调用getEntryAfterMiss()方法
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}
private Entry getEntryAfterMiss(ThreadLocal key, int i, Entry e) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 迭代往后查找key相等的entry
while (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == key)
return e;
// 遇到key=null的entry,先进行探测式清理工作
if (k == null)
expungeStaleEntry(i);
else
i = nextIndex(i, len);
e = tab[i];
}
return null;
}
当散列数组中元素已经超过扩容阙值 len*2/3,会进行扩容
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
扩容机制核心方法:
private void rehash() {
//先进行探测式清理工作
expungeStaleEntries();
//探测式清理完毕之后 如果size >= threshold - threshold / 4(也就是 size >= len * 1/2),则扩容
if (size >= threshold - threshold / 4)
resize();
}
private void expungeStaleEntries() {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
for (int j = 0; j
if (e != null && e.get() == null)
expungeStaleEntry(j);
}
}
所以,主要流程是:
private void resize() {
Entry[] oldTab = table;
int oldLen = oldTab.length;
// tab 的大小变为原先的两倍 oldLen * 2
int newLen = oldLen * 2;
Entry[] newTab = new Entry[newLen];
int count = 0;
// 遍历生成新的散列表
for (int j = 0; j
if (e != null) {
ThreadLocal k = e.get();
if (k == null) {
e.value = null;
} else {
// entry表下标
int h = k.threadLocalHashCode & (newLen - 1);
while (newTab[h] != null)
h = nextIndex(h, newLen);
newTab[h] = e;
count++;
}
}
}
// 重新计算扩容阙值
setThreshold(newLen);
size = count;
table = newTab;
}
public void remove() {
// 获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
private void remove(ThreadLocal key) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
// 获取Entry下标
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
// 从hash获取的下标开始,寻找key相等的entry元素清除
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
if (e.get() == key) {
e.clear();
// 进行探测式清理工作
expungeStaleEntry(i);
return;
}
}
}
前面已经对ThreadLocal进行了浅显的分析,然后在实际工作中如何使用ThreadLocal?
在ThreadLocal源码的注释里,作者已经给出一个例子:
package com.example.concurrent.threadlocal;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ThreadId {
// Atomic integer containing the next thread ID to be assigned
private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);
// Thread local variable containing each thread's ID
private static final ThreadLocal
new ThreadLocal
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return nextId.getAndIncrement();
}
};
// Returns the current thread's unique ID, assigning it if necessary
public static int get() {
return threadId.get();
}
}
我们复制例子运行一下,例子也比较简单,是通过原子类加上ThreadLocal实现的线程安全的计数例子,然后ThreadLocal如何正确使用?
为什么要使用remove?在阿里编程规范里也说明了不remove可能会造成内存泄漏问题,不正确使用可能造成:
private static final ThreadLocal threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
try {
threadLocal.set(a);
//执行业务逻辑,逻辑中 get()值
}finally{
//确保用完后,清除
threadLocal.remove();
}
ThreadLocal对象的数据,不过ThreadLocal是不支持这种情况,需要使用InheritableThreadLocalpackage com.example.concurrent.threadlocal;
public class InheritableThreadLocalSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadLocal
InheritableThreadLocal
t1.set("test1");
t2.set("test2");
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(String.format("获取ThreadLocal数据 %s" , t1.get()));
System.out.println(String.format("获取InheritableThreadLocal数据 %s" , t2.get()));
}).start();
}
}
获取ThreadLocal数据 null
获取InheritableThreadLocal数据 test2

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有