深度卷积网络极大地推进深度学习各领域的发展,ILSVRC作为最具影响力的竞赛功不可没,促使了许多经典工作。我梳理了ILSVRC分类任务的各届冠军和亚军网络,简单介绍了它们的核心思想、网络架构及其实现。
代码主要来自:https://github.com/weiaicunzai/pytorch-cifar100
ImageNet和ILSVRC
ImageNet是一个超过15 million的图像数据集,大约有22,000类。
ILSVRC全称ImageNet Large-Scale Visual Recognition Challenge,从2010年开始举办到2017年最后一届,使用ImageNet数据集的一个子集,总共有1000类。
历届结果
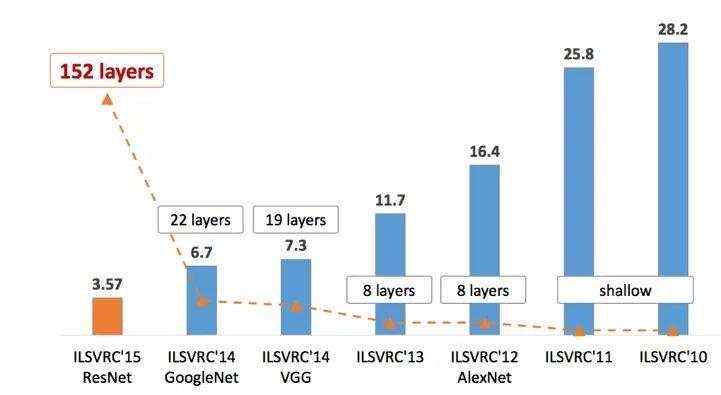
| 年 | 网络/队名 | val top-1 | val top-5 | test top-5 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
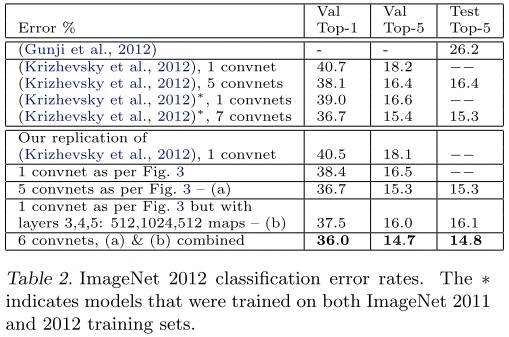
| 2012 | AlexNet | 38.1% | 16.4% | 16.42% | 5 CNNs |
| 2012 | AlexNet | 36.7% | 15.4% | 15.32% | 7CNNs。用了2011年的数据 |
| 2013 | OverFeat | 14.18% | 7 fast models | ||
| 2013 | OverFeat | 13.6% | 赛后。7 big models | ||
| 2013 | ZFNet | 13.51% | ZFNet论文上的结果是14.8 | ||
| 2013 | Clarifai | 11.74% | |||
| 2013 | Clarifai | 11.20% | 用了2011年的数据 | ||
| 2014 | VGG | 7.32% | 7 nets, dense eval | ||
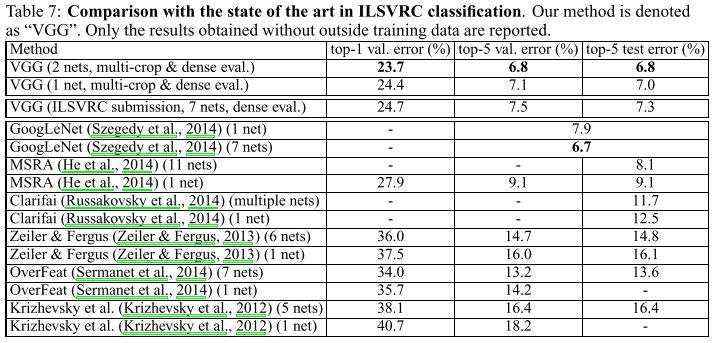
| 2014 | VGG(亚军) | 23.7% | 6.8% | 6.8% | 赛后。2 nets |
| 2014 | GoogleNet v1 | 6.67% | 7 nets, 144 crops | ||
| GoogleNet v2 | 20.1% | 4.9% | 4.82% | 赛后。6 nets, 144 crops | |
| GoogleNet v3 | 17.2% | 3.58% | 赛后。4 nets, 144 crops | ||
| GoogleNet v4 | 16.5% | 3.1% | 3.08% | 赛后。v4+Inception-Res-v2 | |
| 2015 | ResNet | 3.57% | 6 models | ||
| 2016 | Trimps-Soushen | 2.99% | 公安三所 | ||
| 2016 | ResNeXt(亚军) | 3.03% | 加州大学圣地亚哥分校 | ||
| 2017 | SENet | 2.25% | Momenta 与牛津大学 |
评价标准
top1是指概率向量中最大的作为预测结果,若分类正确,则为正确;top5则只要概率向量中最大的前五名里有分类正确的,则为正确。
Gradient-Based Learning Applied to Document Recognition

import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as func
class LeNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self):super(LeNet, self).__init__()self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5)self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16*16, 120)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)def forward(self, x):x = func.relu(self.conv1(x))x = func.max_pool2d(x, 2)x = func.relu(self.conv2(x))x = func.max_pool2d(x, 2)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = func.relu(self.fc1(x))x = func.relu(self.fc2(x))x = self.fc3(x)return x
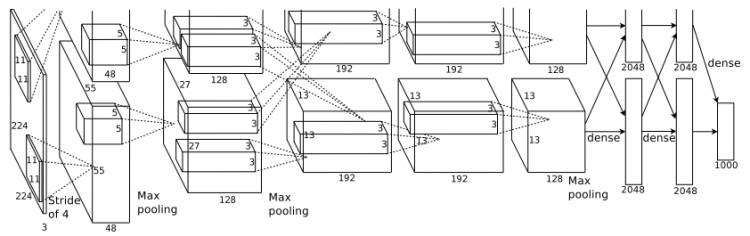
ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
AlexNet相比前人有以下改进:
1.采用ReLU激活函数
2.局部响应归一化LRN

3.Overlapping Pooling
4.引入Drop out
5.数据增强
6.多GPU并行
代码实现
class AlexNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, num_classes=NUM_CLASSES):super(AlexNet, self).__init__()self.features = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11,padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),)self.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(256 * 2 * 2, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Linear(4096, 10),)def forward(self, x):x = self.features(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), 256 * 2 * 2)x = self.classifier(x)return x
Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks
利用反卷积可视化CNN学到的特征。
1.Unpooling:池化操作不可逆,但通过记录池化最大值的位置可实现逆操作。
2.Rectification:ReLU
3.Filtering:使用原卷积核的转置版本。


特征可视化:Layer2响应角落和边缘、颜色连接;Layer3有更复杂的不变性,捕获相似纹理;Layer4展示了明显的变化,跟类别更相关;Layer5看到整个物体。

训练过程特征演化:低层特征较快收敛,高层到后面才开始变化。

特征不变性:小变换在模型第一层变化明显,但在顶层影响较小。网络输出对翻转和缩放是稳定的,但除了旋转对称性的物体,输出对旋转并不是不变的。
遮挡敏感性:当对象被遮挡,准确性会明显下降。
ImageNet结果
Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition
重复使用3x3卷积和2x2池化增加网络深度。
VGG19表示有19层conv或fc,参数量较大。

代码实现
cfg = {'A' : [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],'B' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],'D' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],'E' : [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M']
}def vgg19_bn():return VGG(make_layers(cfg['E'], batch_norm=True))class VGG(nn.Module):def __init__(self, features, num_class=100):super().__init__()self.features = featuresself.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, 4096),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, num_class))def forward(self, x):output = self.features(x)output = output.view(output.size()[0], -1)output = self.classifier(output)return outputdef make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):layers = []input_channel = 3for l in cfg:if l == 'M':layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]continuelayers += [nn.Conv2d(input_channel, l, kernel_size=3, padding=1)]if batch_norm:layers += [nn.BatchNorm2d(l)]layers += [nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]input_channel = lreturn nn.Sequential(*layers)
Going Deeper with Convolutions
提出Inception模块,可在保持计算成本的同时增加网络的深度和宽度。

代码实现
class Inception(nn.Module):def __init__(self, input_channels, n1x1, n3x3_reduce, n3x3, n5x5_reduce, n5x5, pool_proj):super().__init__()#1x1conv branchself.b1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(input_channels, n1x1, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n1x1),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#1x1conv -> 3x3conv branchself.b2 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(input_channels, n3x3_reduce, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n3x3_reduce),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(n3x3_reduce, n3x3, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n3x3),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#1x1conv -> 5x5conv branch#we use 2 3x3 conv filters stacked instead#of 1 5x5 filters to obtain the same receptive#field with fewer parametersself.b3 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(input_channels, n5x5_reduce, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5_reduce),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(n5x5_reduce, n5x5, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5, n5x5),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(n5x5, n5x5, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(n5x5),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#3x3pooling -> 1x1conv#same convself.b4 = nn.Sequential(nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=1, padding=1),nn.Conv2d(input_channels, pool_proj, kernel_size=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(pool_proj),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))def forward(self, x):return torch.cat([self.b1(x), self.b2(x), self.b3(x), self.b4(x)], dim=1)


代码实现
def googlenet():return GoogleNet()class GoogleNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, num_class=100):super().__init__()self.prelayer = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 192, kernel_size=3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(192),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#although we only use 1 conv layer as prelayer,#we still use name a3, b3.......self.a3 = Inception(192, 64, 96, 128, 16, 32, 32)self.b3 = Inception(256, 128, 128, 192, 32, 96, 64)#"""In general, an Inception network is a network consisting of#modules of the above type stacked upon each other, with occasional#max-pooling layers with stride 2 to halve the resolution of the#grid"""self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2, padding=1)self.a4 = Inception(480, 192, 96, 208, 16, 48, 64)self.b4 = Inception(512, 160, 112, 224, 24, 64, 64)self.c4 = Inception(512, 128, 128, 256, 24, 64, 64)self.d4 = Inception(512, 112, 144, 288, 32, 64, 64)self.e4 = Inception(528, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)self.a5 = Inception(832, 256, 160, 320, 32, 128, 128)self.b5 = Inception(832, 384, 192, 384, 48, 128, 128)#input feature size: 8*8*1024self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(p=0.4)self.linear = nn.Linear(1024, num_class)def forward(self, x):output = self.prelayer(x)output = self.a3(output)output = self.b3(output)output = self.maxpool(output)output = self.a4(output)output = self.b4(output)output = self.c4(output)output = self.d4(output)output = self.e4(output)output = self.maxpool(output)output = self.a5(output)output = self.b5(output)#"""It was found that a move from fully connected layers to#average pooling improved the top-1 accuracy by about 0.6%,#however the use of dropout remained essential even after#removing the fully connected layers."""output = self.avgpool(output)output = self.dropout(output)output = output.view(output.size()[0], -1)output = self.linear(output)return output

Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
为了解决深层网络难以训练的问题,提出了残差模块和深度残差网络
1.假设网络输入是x,经学习的输出是F(x),最终拟合目标是H(x)。
2.深层网络相比浅层网络有一些层是多余的,若让多余层学习恒等变换H(x)=x,那么网络性能不该比浅层网络要差。
3.传统网络训练目标H(x)=F(x),残差网络训练目标H(x)=F(x)+x。
4.为了学习恒等变换,传统网络要求网络学习F(x)=H(x)=x,残差网络只需学习 F(x)=H(x)−x=x−x=0。残差学习之所以有效是因为让网络学习F(x)=0比学习F(x)=x要容易。

bottleneck

代码实现
class BottleNeck(nn.Module):"""Residual block for resnet over 50 layers"""expansion = 4def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):super().__init__()self.residual_function = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, stride=stride, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * BottleNeck.expansion, kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * BottleNeck.expansion),)self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels * BottleNeck.expansion:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels * BottleNeck.expansion, stride=stride, kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * BottleNeck.expansion))def forward(self, x):return nn.ReLU(inplace=True)(self.residual_function(x) + self.shortcut(x))


代码实现
def resnet152():""" return a ResNet 152 object"""return ResNet(BottleNeck, [3, 8, 36, 3])class ResNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, num_block, num_classes=100):super().__init__()self.in_channels = 64self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))#we use a different inputsize than the original paper#so conv2_x's stride is 1self.conv2_x = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_block[0], 1)self.conv3_x = self._make_layer(block, 128, num_block[1], 2)self.conv4_x = self._make_layer(block, 256, num_block[2], 2)self.conv5_x = self._make_layer(block, 512, num_block[3], 2)self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, block, out_channels, num_blocks, stride):"""make resnet layers(by layer i didnt mean this 'layer' was thesame as a neuron netowork layer, ex. conv layer), one layer maycontain more than one residual blockArgs:block: block type, basic block or bottle neck blockout_channels: output depth channel number of this layernum_blocks: how many blocks per layerstride: the stride of the first block of this layerReturn:return a resnet layer"""# we have num_block blocks per layer, the first block# could be 1 or 2, other blocks would always be 1strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_blocks - 1)layers = []for stride in strides:layers.append(block(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride))self.in_channels = out_channels * block.expansionreturn nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):output = self.conv1(x)output = self.conv2_x(output)output = self.conv3_x(output)output = self.conv4_x(output)output = self.conv5_x(output)output = self.avg_pool(output)output = output.view(output.size(0), -1)output = self.fc(output)return output

Aggregated Residual Transformations for Deep Neural Networks
通过重复构建block来聚合一组相同拓扑结构的特征,并提出一个新维度”cardinality“。
ResNeXt结合了VGG、ResNet重复堆叠模块和Inception的split-transform-merge的思想。

以下三者等价,文章采用第三种实现,其使用了组卷积。

代码实现
CARDINALITY = 32
DEPTH = 4
BASEWIDTH = 64class ResNextBottleNeckC(nn.Module):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride):super().__init__()C = CARDINALITY #How many groups a feature map was splitted into#"""We note that the input/output width of the template is fixed as#256-d (Fig. 3), We note that the input/output width of the template#is fixed as 256-d (Fig. 3), and all widths are dou- bled each time#when the feature map is subsampled (see Table 1)."""D = int(DEPTH * out_channels / BASEWIDTH) #number of channels per groupself.split_transforms = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, C * D, kernel_size=1, groups=C, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(C * D),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(C * D, C * D, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, groups=C, padding=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(C * D),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(C * D, out_channels * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * 4),)self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels * 4:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels * 4, stride=stride, kernel_size=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * 4))def forward(self, x):return F.relu(self.split_transforms(x) + self.shortcut(x))

代码实现
以下部分跟ResNet基本一致,重点关注ResNextBottleNeckC的实现。
def resnext50():""" return a resnext50(c32x4d) network"""return ResNext(ResNextBottleNeckC, [3, 4, 6, 3])class ResNext(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, class_names=100):super().__init__()self.in_channels = 64self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.conv2 = self._make_layer(block, num_blocks[0], 64, 1)self.conv3 = self._make_layer(block, num_blocks[1], 128, 2)self.conv4 = self._make_layer(block, num_blocks[2], 256, 2)self.conv5 = self._make_layer(block, num_blocks[3], 512, 2)self.avg = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * 4, 100)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.conv2(x)x = self.conv3(x)x = self.conv4(x)x = self.conv5(x)x = self.avg(x)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.fc(x)return xdef _make_layer(self, block, num_block, out_channels, stride):"""Building resnext blockArgs:block: block type(default resnext bottleneck c)num_block: number of blocks per layerout_channels: output channels per blockstride: block strideReturns:a resnext layer"""strides = [stride] + [1] * (num_block - 1)layers = []for stride in strides:layers.append(block(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride))self.in_channels = out_channels * 4return nn.Sequential(*layers)

Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks
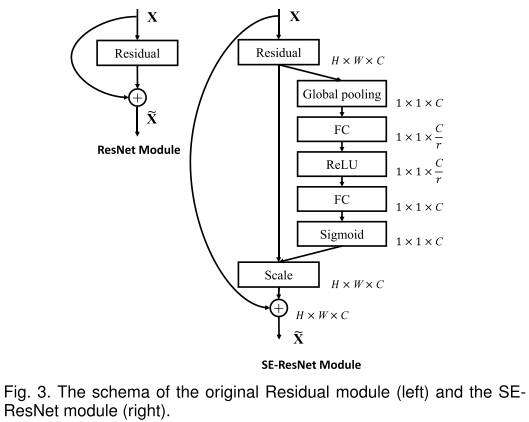
卷积操作融合了空间和特征通道信息。大量工作研究了空间部分,而本文重点关注特征通道的关系,并提出了Squeeze-and-Excitation(SE)block,对通道间的依赖关系进行建模,自适应校准通道方面的特征响应。
SE block
 表示transformation(一系列卷积操作);
表示transformation(一系列卷积操作); 表示squeeze,产生通道描述;
表示squeeze,产生通道描述; 表示excitation,通过参数WW来建模通道的重要性。
表示excitation,通过参数WW来建模通道的重要性。 表示reweight,将excitation输出的权重逐乘以先前特征,完成特征重标定。
表示reweight,将excitation输出的权重逐乘以先前特征,完成特征重标定。

SE-ResNet Module
代码实现
class BottleneckResidualSEBlock(nn.Module):expansion = 4def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride, r=16):super().__init__()self.residual = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, 3, stride=stride, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels * self.expansion, 1),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * self.expansion),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.squeeze = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)self.excitation = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(out_channels * self.expansion, out_channels * self.expansion // r),nn.ReLU(inplace=True),nn.Linear(out_channels * self.expansion // r, out_channels * self.expansion),nn.Sigmoid())self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels * self.expansion:self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels * self.expansion, 1, stride=stride),nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels * self.expansion))def forward(self, x):shortcut = self.shortcut(x)residual = self.residual(x)squeeze = self.squeeze(residual)squeeze = squeeze.view(squeeze.size(0), -1)excitation = self.excitation(squeeze)excitation = excitation.view(residual.size(0), residual.size(1), 1, 1)x = residual * excitation.expand_as(residual) + shortcutreturn F.relu(x)

代码实现
def seresnet50():return SEResNet(BottleneckResidualSEBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3])class SEResNet(nn.Module):def __init__(self, block, block_num, class_num=100):super().__init__()self.in_channels = 64self.pre = nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2d(3, 64, 3, padding=1),nn.BatchNorm2d(64),nn.ReLU(inplace=True))self.stage1 = self._make_stage(block, block_num[0], 64, 1)self.stage2 = self._make_stage(block, block_num[1], 128, 2)self.stage3 = self._make_stage(block, block_num[2], 256, 2)self.stage4 = self._make_stage(block, block_num[3], 516, 2)self.linear = nn.Linear(self.in_channels, class_num)def forward(self, x):x = self.pre(x)x = self.stage1(x)x = self.stage2(x)x = self.stage3(x)x = self.stage4(x)x = F.adaptive_avg_pool2d(x, 1)x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)x = self.linear(x)return xdef _make_stage(self, block, num, out_channels, stride):layers = []layers.append(block(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride))self.in_channels = out_channels * block.expansionwhile num - 1:layers.append(block(self.in_channels, out_channels, 1))num -= 1return nn.Sequential(*layers)

一、小结
1.LeNet[1998]:CNN的鼻祖。
2.AlexNet[2012]:第一个深度CNN。
3.ZFNet[2012]:通过DeconvNet可视化CNN学习到的特征。
4.VGG[2014]:重复堆叠3x3卷积增加网络深度。
5.GoogLeNet[2014]:提出Inception模块,在控制参数和计算量的前提下,增加网络的深度与宽度。
6.ResNet[2015]:提出残差网络,解决了深层网络的优化问题。
7.ResNeXt[2016]:ResNet和Inception的结合体,Inception中每个分支结构相同,无需人为设计。
8.SENet[2017]:提出SE block,关注特征的通道关系。
二、经典模型中结构、参数对比

paper
[1]LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324.
[2]Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in neural information processing systems. 2012: 1097-1105.
[3]Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//European conference on computer vision. springer, Cham, 2014: 818-833.
[4]Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556, 2014.
[5]Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2015: 1-9.
[6]He K, Zhang X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2016: 770-778.
[7]Xie S, Girshick R, Dollár P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2017: 1492-1500.
[8]Hu J, Shen L, Sun G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. 2018: 7132-7141.
blog
ImageNet历年冠军和相关CNN模型
残差网络ResNet笔记
(二)计算机视觉四大基本任务(分类、定位、检测、分割)
论文笔记:CNN经典结构2(WideResNet,FractalNet,DenseNet,ResNeXt,DPN,SENet)
论文笔记:CNN经典结构1(AlexNet,ZFNet,OverFeat,VGG,GoogleNet,ResNet)
深度学习在计算机视觉领域(包括图像,视频,3-D点云,深度图)的应用一览
(本文出自平台合作作者Vincent,cs硕士在读。)
不断更新资源
获取更多精彩
长按二维码扫码关注


 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有