spring mvc可以说是大部分小伙伴做web项目的第一个使用到的框架,当然如果比较久远的话大家还会学到structs或structs2,不过有一些原因被淘汰了。之前用SSH也逐步转变成了SSM框架。当然目前到了微服务项目也离不开它,唯一不同的是前后端分离了,基本不需要他的视图。当然小编还是会带过他是视图。
今天为了大家带来spring mvc的整体架构以及核心流程。咱们进入正题
在刚刚学习java企业应用级应用的时候,咱们首先学到的是Servlet,那其实spring mvc是基于他来封装开发的,那咱们先来回顾他的流程
先看一下下图:
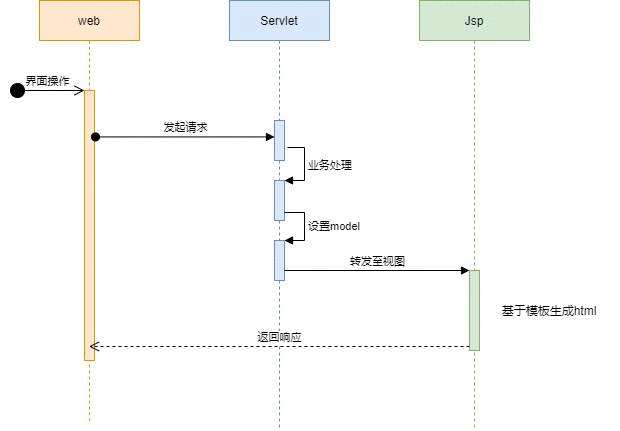
看了上图,其实流程比较简单一目了然,那web怎么到达Servlet以及Servlet怎么到达Jsp的,他的本质又是什么?这里涉及到一些知识。
当然这个不是重点,接下来我们看一下spring mvc的流程
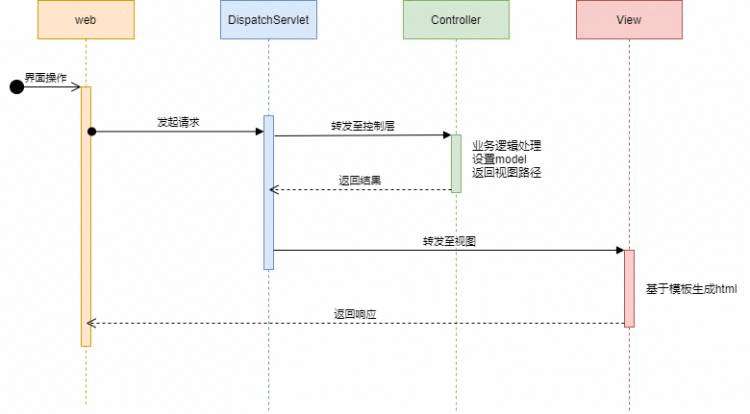
其实和Servlet差不多,但是多出了Controller层,将业务逻辑交给了Controller,之后返回给DispatchServlet再转发给View,然后基于模板生成html再返回给浏览器。
那spring mvc为什么要加上控制层,相较于servlet流程有哪些优点,那咱们继续往下看。
传统的映射体系,学习servlet的时候大家应该知道,我们配置一个映射的话,基本就是xx/xx.do,这样映射比较麻烦,第二是传递的参数,参数获取或封装都比较麻烦,第三就是servlet请求如果有多个就需要有多个servlet来处理。还有其他的问题,基于上面的种种问题,那spring mvc进行了优化。那首先我们看一下他的体系结构图:
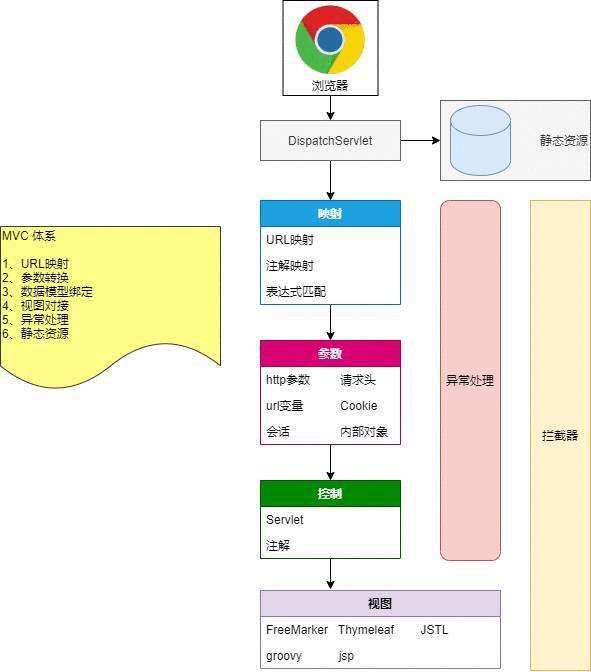
优点:
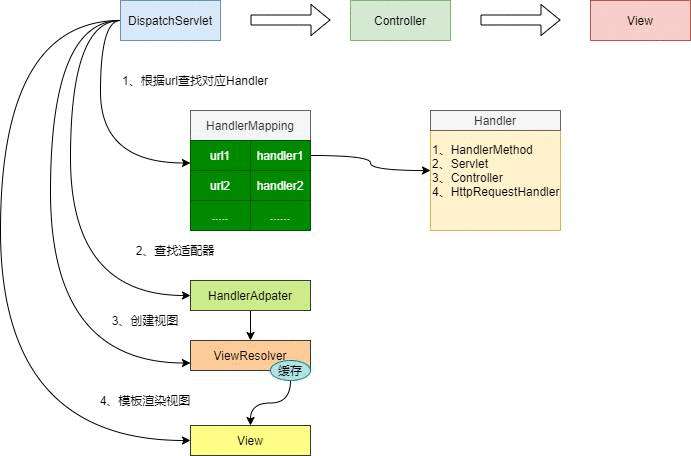
看了体系结构,那我们看一下他的核心流程以及细节。这里会涉及他的源码:
这里演示的是平常不太用到的
**Servlet**
```java
@Controller("/servlet")
public class ServletHandler extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("hello luban uncle");
}
}
@Component
public class ServletHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter {
@Override
public boolean supports(Object handler) {
return (handler instanceof Servlet);
}
@Override
public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
((Servlet) handler).service(request, response);
return null;
}
@Override
public long getLastModified(HttpServletRequest request, Object handler) {
return -1;
}
}
值得注意的是Servlet需要加上对应的适配器,因为servlet没有自己的适配得手工加上,如果不加则会报错
javax.servlet.ServletException: javax.servlet.ServletException: No adapter for handler [com.lecture.mvc.ServletHandler@409c7566]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler
其他的为什么不用加,想必大家已经明白了,因为spring对大多数已经自动加入了handlerAdapter,不需要手动加进去。
具体是在springwebmvc的jar下面的DispatcherServlet.properties文件。
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
controller
@Component("/hi")
public class ControllerHandler implements Controller {
@Override
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
//viewResolver
ModelAndView userView = new ModelAndView("userView");
userView.addObject("name","hello");
return userView;
}
}
**HttpRequestHandler**
```java
public class HttpRequestHandlerTest implements HttpRequestHandler {
@Override
public void handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws ServletException, IOException {
httpServletResponse.getWriter().write("hello world http request handler");
}
}
看到这儿大家是否觉得有疑问,那为什么没有HandlerMethod的代码示例,这个暂且不表,小编后续会说明。
实际过程中controller和HttpRequestHandler在实际过程中99%是不会用到的,那为什么会有这两个呢,主要是为了动态扩展Handler,这两种bean,直接可以放入spring的ioc容器里面。
接下来小编看一下他的初始化过程。
上面的HandlerMapping,HandlerAdpater,ViewResolver以及View本质上都是Bean,并被spring Ioc容器所管理,那这些bean怎么被DispatchServlet所使用的呢,其实很简单,他在启动的时候找出上面的Bean并且添加进去,那这样DispatchServlet必须有初始化的动作。下图看DispatchServlet中包含哪些:
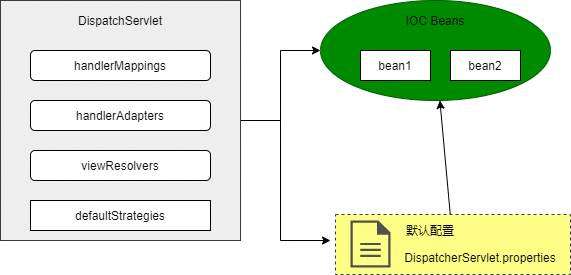
从上图可看出中DispatchServlet组件中包含多个HandlerMapping,HandlerAdpater以及ViewResolver,当然大家是否有疑问怎么没有View了,其实View是动态生成的,然后看一下源码:
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context);
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化HandlerMappings
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
//初始化HandlerAdapters
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化HandlerAdapters
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}
大家先不需要关心其他的组件,因为不属于核心组件。这里初始化的源码咱们只看一个initHandlerMappings,因为其他的init都相差不大,很简单
initHandlerMappings
private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {
this.handlerMappings = null;
if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {
// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.
//找到容器中所以的HandlerMappings
Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans =
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);
if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
//设置进去
this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());
// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order. 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);
}
}
else {
try {
HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);
this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.
}
}
// Ensure we have at least one HandlerMapping, by registering
// a default HandlerMapping if no other mappings are found.
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//都为空则去找配置文件内容,就去找对应的文件
this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No HandlerMappings declared for servlet '" + getServletName() +
"': using default strategies from DispatcherServlet.properties");
}
}
}
这样组件初始化就完成了。接下来初始化后怎么调用到他。那接着看一下调用的流程以及源码。
首先调用的时序图如下:
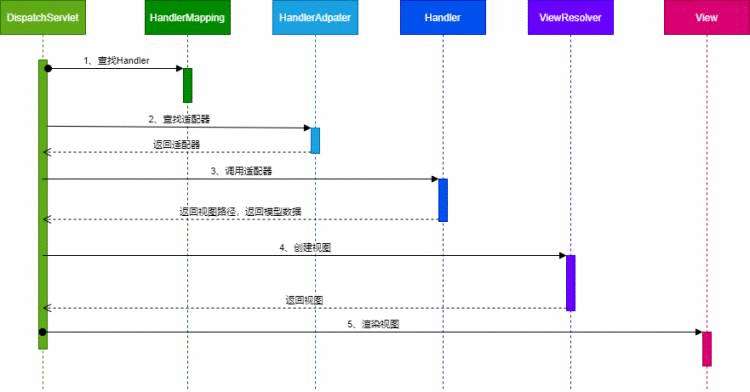
时序图非常简单,那咱们看一下源码:
首先不管是post还是get最终都回到这个org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet#doService
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
.......
try {
//调用到doDispatch方法
doDispatch(request, response);
}
.....
}
doDispatch
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// Determine handler for the current request.
//找到我们的handler,也就是从handlerMappings中找到我们的映射
//拿到的是HandlerExecutionChain 里面包装了Handler,里面使用HandlerExecutionChain
//主要里面有需要执行的拦截器的方法
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// Determine handler adapter for the current request.
//找到我们的handler适配器,handlerAdapters里面查找,如果找不到直接报错
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//找到适配器后首先是执行前置拦截方法,看是否被拦截
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
//真正调用Handler根据适配器发起调用,返回了modelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
//设置viewName
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//后置处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
//这里是创建视图并渲染
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
创建视图org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractCachingViewResolver#resolveViewName
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
//不使用缓存直接创建
if (!isCache()) {
return createView(viewName, locale);
}
else {
//双重锁检测
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(viewName, locale);
View view = this.viewAccessCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
synchronized (this.viewCreationCache) {
view = this.viewCreationCache.get(cacheKey);
if (view == null) {
// Ask the subclass to create the View object.
view = createView(viewName, locale);
if (view == null && this.cacheUnresolved) {
view = UNRESOLVED_VIEW;
}
if (view != null) {
//这里因为view是有容量的,这里viewCreationCache使用了LinkedHashMap
//这边满了之后会溢出淘汰最近最少使用LRU
this.viewAccessCache.put(cacheKey, view);
this.viewCreationCache.put(cacheKey, view);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatKey(cacheKey) + "served from cache");
}
}
return (view != UNRESOLVED_VIEW ? view : null);
}
}
渲染视图 也就是讲model作为属性填充到request,然后request进行forward转发
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.AbstractView#render
public void render(@Nullable Map<String, ?> model, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("View " + formatViewName() +
", model " + (model != null ? model : Collections.emptyMap()) +
(this.staticAttributes.isEmpty() ? "" : ", static attributes " + this.staticAttributes));
}
Map<String, Object> mergedModel = createMergedOutputModel(model, request, response);
prepareResponse(request, response);
renderMergedOutputModel(mergedModel, getRequestToExpose(request), response);
}
org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceView#renderMergedOutputModel
protected void renderMergedOutputModel(
Map<String, Object> model, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Expose the model object as request attributes.
//填充模型
exposeModelAsRequestAttributes(model, request);
// Expose helpers as request attributes, if any.
exposeHelpers(request);
// Determine the path for the request dispatcher.
String dispatcherPath = prepareForRendering(request, response);
// Obtain a RequestDispatcher for the target resource (typically a JSP).
RequestDispatcher rd = getRequestDispatcher(request, dispatcherPath);
if (rd == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not get RequestDispatcher for [" + getUrl() +
"]: Check that the corresponding file exists within your web application archive!");
}
// If already included or response already committed, perform include, else forward.
if (useInclude(request, response)) {
response.setContentType(getContentType());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Including [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.include(request, response);
}
else {
// Note: The forwarded resource is supposed to determine the content type itself.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Forwarding to [" + getUrl() + "]");
}
rd.forward(request, response);
}
}
看源码的话可能不是那么容易,希望大家调试一遍那就啥都明白了。
小编好久没有写ssm框架,然后又web.xml以及dispatchServlet的配置了,手好生疏,但是这个不是重点,重点是我们能够了解里面对应的代码,以及整体的流程即可。这里虽然有一些即使用了那么多年的spring也没接触到一些内容,比方说HttpRequestHandler ,其实他和@ResponseBody注解相似。
这里主要是回顾spring mvc,让大家知道怎么用以及为什么这么用。包括之前为什么我们要在spring.xml中配置HandlerAdpater。源码阅读还是枯燥的。希望再接再厉,吃透ssm的常用方法及框架。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有