1、Netty 是一个 基于 NIO 的 client-server(客户端服务器)框架,使用它可以快速简单地开发网络应用程序。
2、它极大地简化并优化了 TCP 和 UDP 套接字服务器等网络编程,并且性能以及安全性等很多方面甚至都要更好。
3、支持多种协议 如 FTP,SMTP,HTTP 以及各种二进制和基于文本的传统协议。
用官方的总结就是:Netty 成功地找到了一种在不妥协可维护性和性能的情况下实现易于开发,性能,稳定性和灵活性的方法。
除了上面之外,很多开源项目比如我们常用的 Dubbo、RocketMQ、Elasticsearch、gRPC 等等都用到了 Netty。
当需要连接客户端或者服务器绑定指定端口是需要使用Bootstrap,ServerBootstrap有两种类型,一种是用于客户端的Bootstrap,一种是用于服务端 的ServerBootstrap。不管程序使用哪种协议,无论是创建一个客户端还是服务器都需要使 用“引导”。
Bootstrap 是客户端的启动引导类/辅助类
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try { //创建客户端启动引导/辅助类:Bootstrap Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap(); //指定线程模型 b.group(group). ...... // 尝试建立连接 ChannelFuture f = b.connect(host, port).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally { // 优雅关闭相关线程组资源 group.shutdownGracefully();
}
ServerBootstrap 客户端的启动引导类/辅助类
// 1.bossGroup 用于接收连接,workerGroup 用于具体的处理
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try { //2.创建服务端启动引导/辅助类:ServerBootstrap ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); //3.给引导类配置两大线程组,确定了线程模型 b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup). ...... // 6.绑定端口 ChannelFuture f = b.bind(port).sync(); // 等待连接关闭 f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally { //7.优雅关闭相关线程组资源 bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
Bootstrap 通常使用 connet() 方法连接到远程的主机和端口,作为一个 Netty TCP 协议通信中的客户端。另外,Bootstrap 也可以通过 bind() 方法绑定本地的一个端口,作为 UDP 协议通信中的一端。
ServerBootstrap通常使用 bind() 方法绑定本地的端口上,然后等待客户端的连接。
Bootstrap 只需要配置一个线程组— EventLoopGroup,而 ServerBootstrap需要配置两个线程组— EventLoopGroup ,一个用于接收连接,一个用于具体的处理。
| 分类 | Bootstrap | ServerBootstrap |
|---|---|---|
| 网络功能 | 连接到远程主机和端口 | 绑定本地端口 |
| EventLoopGroup 数量 | 1 | 2 |
一个 ServerBootstrap 可以认为有2个 Channel 集合,
第一个集合包含一个单例 ServerChannel,代表持有一个绑定了本地端口的 socket;
第二集合包含所有创建的 Channel,处理服务器所接收到的客户端进来的连接。
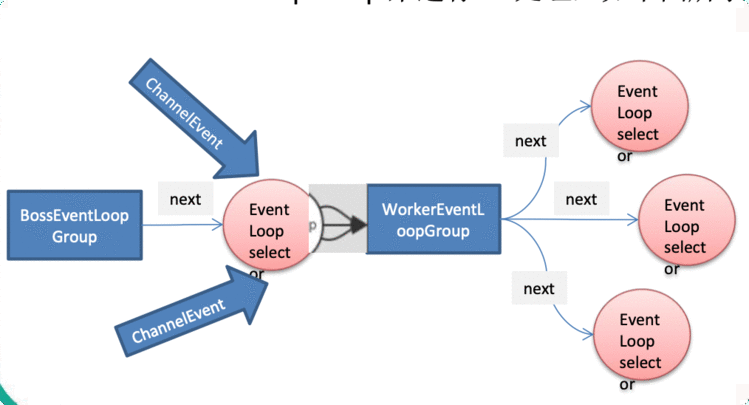
EventLoop 定义了 Netty 的核心抽象,用于处理连接的生命周期中所发生的事件。
EventLoop 的主要作用实际就是负责监听网络事件并调用事件处理器进行相关 I/O 操作的处理。
Channel 和 EventLoop 直接有啥联系呢?
Channel 为 Netty 网络操作(读写等操作)抽象类,EventLoop 负责处理注册到其上的Channel 处理 I/O 操作,两者配合参与 I/O 操作。
EventLoopGroup包含多个EventLoop,每个EventLoop通常内部包含一个线程。EventLoop在处理IO事件时在自己的Thread线程上进行,从而保证线程安全
NioEventLoopGroup在未指定线程数时,默认时当前cpu线程数*2
EventLoop继承图
Channel 接口是 Netty 对网络操作抽象类,它除了包括基本的 I/O 操作,如 bind()、connect()、read()、write() 等。
比较常用的Channel接口实现类是NioServerSocketChannel(服务端)和NioSocketChannel(客户端),这两个 Channel 可以和 BIO 编程模型中的ServerSocket以及Socket两个概念对应上。Netty 的 Channel 接口所提供的 API,大大地降低了直接使用 Socket 类的复杂性。
Channel channel = ...; // 获取channel的引用
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("your data", CharsetUtil.UTF_8); //1 ChannelFuture cf = channel.writeAndFlush(buf); //2
cf.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() { //3
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) {
if (future.isSuccess()) { //4
} });
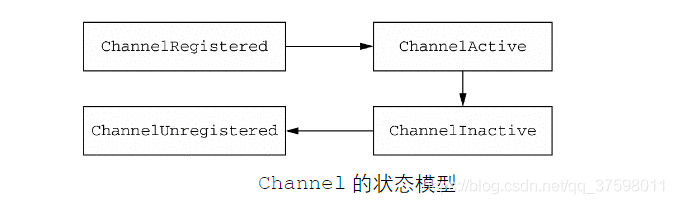
channel声明周期
| 状态 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ChannelUnregistered | Channel 已经被创建,但还未注册到EventLoop |
| ChannelRegistered | Channel 已经被注册到了EventLoop |
| ChannelActive | Channel 处于活动状态(已经连接到它的远程节点)。它现在可以接收和发送数据了 |
| ChannelInactive | Channel 没有连接到远程节点 |
作用:
SelectonKey 状态

ChannelHandler是消息的处理器,负责读写操作和客户端连接等。
ChannelPipeline 为 ChannelHandler 的链,提供了一个容器并定义了用于沿着链传播入站和出站事件流的 API 。当 Channel 被创建时,它会被自动地分配到它专属的 ChannelPipeline。
可以在 ChannelPipeline 上通过 addLast() 方法添加一个或者多个ChannelHandler ,因为一个数据或者事件可能会被多个 Handler 处理。当一个 ChannelHandler 处理完之后就将数据交给下一个 ChannelHandler 。
Netty 发送消息有两种方式。您可以直接写消息给 Channel 或写入 ChannelHandlerContext 对象。主要的区别是, 前一种方法会导致消息从 ChannelPipeline的 尾部开始,而 后者导致消息从 ChannelPipeline 下一个处理器开始。
ChannelHandler的子接口:
HttpClientCodec和HttpServerCodec:HttpClientCodec负责将请求字节码解码为HttpRequest、HttpContent和LastHttpContent消息,以及对应的转为字节;HttpServerCodec负责服务端中将字节码解析成HttpResponse、HttpContent和LastHttpContent消息,以及对应的将它转为字节。
HttpServerCodec 里面组合了HttpResponseEncoder和HttpRequestDecoder
HttpClientCodec 里面组合了HttpRequestEncoder和HttpResponseDecoder
HttpObjectAggregate:负责将http聚合成完整的消息,而不是原始的多个部分。
HttpContentCompressor和HttpContentDecompressor:HttpContentCompressor用于服务器压缩数据,HttpContentDecompressor用于客户端解压数据
IdleStateHandler:连接空闲时间过长,触发IdleStateEvent事件
ReadTimeoutHandler:指定时间内没有收到任何入站数据,抛出ReadTimeoutException异常,关闭Channel。
WriteTimeoutHandler:指定时间内没有收到任何出站数据写入,抛出WriteTimeoutException异常,关闭Channel。
DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder:使用任何用户提供的分隔符来提取帧的通用解码器。
FixedLengthFrameDecoder:提取在调用构造函数时的定长帧。
ChuckedWriterHandler:将大型文件从文件系统复制到内存【DefaultFileRegion进行大型文件传输】
注意:
ChannelHandler实例如果带有 @Sharable注解则可以被添加到多个ChannelPipeline。也就是说单个ChannelHandler实例可以有多个ChannelHandlerContext,因此可以调用不同ChannelHandlerContext获取同一个ChannelHandler。如果添加不带@Sharable注解的ChannelHandler实例到多个ChannelPipeline则会抛出异常;使用@Sharable注解后的ChannelHandler必须在不同的线程和不同的通道上安全使用。ChannelHandler实例如果带有@Sharable注解则可以被添加到多个ChannelPipeline。也就是说单个ChannelHandler实例可以有多个ChannelHandlerContext,因此可以调用不同ChannelHandlerContext获取同一个ChannelHandler。如果添加不带@Sharable注解的ChannelHandler实例到多个ChannelPipeline则会抛出异常;使用@Sharable注解后的ChannelHandler必须在不同的线程和不同的通道上安全使用。
出站操作和数据将由ChannelOutboundHandler处理。它的方法将被Channel、ChannelPipeline以及ChannelHandlerContext调用。ChannelOutboundHandler的一个强大的功能是可以按需推迟操作或者事件,这使得可以通过一些复杂的方法来处理请求。例如,如果到远程节点的写入被暂停了,那么你可以推迟冲刷操作并在稍后继续。
public interface ChannelOutboundHandler extends ChannelHandler {/**当请求将Channel绑定到本地地址时被调用/void bind(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求将Channel连接到远程节点时被调用/void connect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, SocketAddress remoteAddress,SocketAddress localAddress, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求将Channel从远程节点断开时被调用/void disconnect(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求关闭Channel时被调用/void close(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求将Channel从它的EventLoop注销时被调用/void deregister(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求从Channel读取更多的数据时被调用/void read(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当请求通过Channel将数据写到远程节点时被调用/void write(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg, ChannelPromise promise) throws Exception;/**当请求通过Channel将入队数据冲刷到远程节点时被调用/void flush(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;}
/**{@link ChannelHandler} which adds callbacks for state changes. This allows the userto hook in to state changes easily./public interface ChannelInboundHandler extends ChannelHandler {/**当Channel已经注册到它的EventLoop并且能够处理I/O时被调用/void channelRegistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当Channel从它的EventLoop注销并且无法处理任何I/O时被调用/void channelUnregistered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当Channel处于活动状态时被调用;Channel已经连接/绑定并且已经就绪/void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当Channel离开活动状态并且不再连接它的远程节点时被调用/void channelInactive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当从Channel读取数据时被调用/void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception;/**当Channel上的一个读操作完成时被调用/void channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**当ChannelnboundHandler.fireUserEventTriggered()方法被调用时被调用,因为一个POJO被传经了ChannelPipeline/void userEventTriggered(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object evt) throws Exception;/**当Channel的可写状态发生改变时被调用。用户可以确保写操作不会完成得太快(以避免发生OutOfMemoryError)或者可以在Channel变为再次可写时恢复写入。可以通过调用Channel的isWritable()方法来检测Channel的可写性。与可写性相关的阈值可以通过Channel.config().setWriteHighWaterMark()和Channel.config().setWriteLowWater-Mark()方法来设置/void channelWritabilityChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception;/**如果抛出一个可抛出的异常对象,则调用。/@Override@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception;}
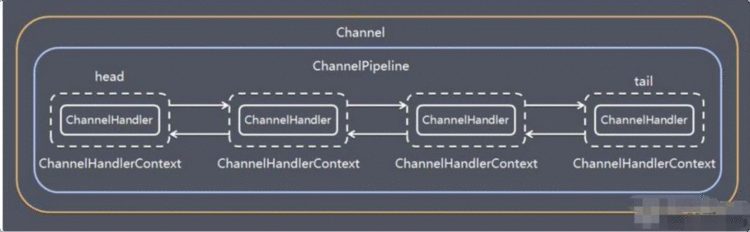
一个channel对应一个pipeline,一个pipeline对应n个ChannelHandler
ChannelPipeline 调度 handler
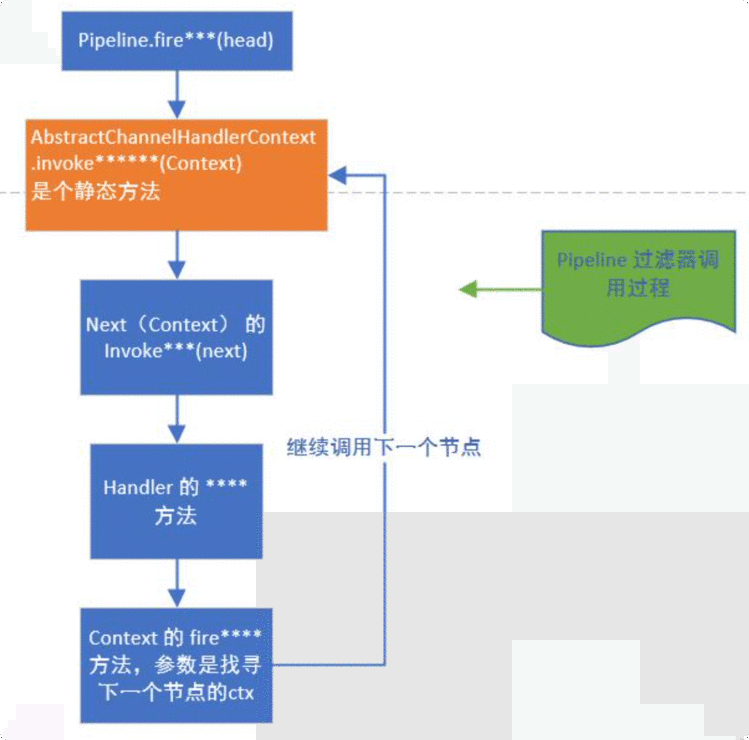
ChannelHandlerContext代表了ChannelHandler和ChannelPipeline之间的关联,每当有ChannelHandler添加到ChannelPipeline中时,都会创建ChannelHandlerContext。ChannelHandlerContext的主要功能是管理它所关联的ChannelHandler和在同一个ChannelPipeline中的其他ChannelHandler之间的交互。
ChannelHandlerContext有很多的方法,其中一些方法也存在于Channel和ChannelPipeline本身上,但是有一点重要的不同。如果调用Channel或者ChannelPipeline上的这些方法,它们将沿着整个ChannelPipeline进行传播。而调用位于ChannelHandlerContext上的相同方法,则将从当前所关联的ChannelHandler开始,并且只会传播给位于该ChannelPipeline中的下一个能够处理该事件的ChannelHandler。
public interface ChannelHandlerContext extends AttributeMap, ChannelInboundInvoker, ChannelOutboundInvoker {/*** 返回绑定到这个实例的Channel*/Channel channel();/*** 返回调度事件的EventExecutor*/EventExecutor executor();/*** 返回这个实例的唯一名称*/String name();/*** 返回绑定到这个实例的ChannelHandler*/ChannelHandler handler();/*** 如果所关联的ChannelHandler已经被从ChannelPipeline中移除则返回true*/boolean isRemoved();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelRegistered()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelUnregistered()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelUnregistered();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelActive()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelActive();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelInactive()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelInactive();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireExceptionCaught()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireExceptionCaught(Throwable cause);/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireUserEventTriggered()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireUserEventTriggered(Object evt);/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelRead()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(Object msg);/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelReadComplete()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelReadComplete();/*** 触发对下一个ChannelInboundHandler上的fireChannelWritabilityChanged()方法的调用*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext fireChannelWritabilityChanged();/*** 将数据从Channel读取到第一个入站缓冲区;如果读取成功则触发一个channelRead事件,并(在最后一个消息被读取完成后)通知ChannelInboundHandler的channelReadComplete(ChannelHandlerContext)方法*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext read();/*** 刷新所有挂起的消息。*/@OverrideChannelHandlerContext flush();/*** 返回这个实例所关联的ChannelPipeline*/ChannelPipeline pipeline();/*** 返回和这个实例相关联的Channel所配置的ByteBufAllocator*/ByteBufAllocator alloc();/******************补充*************************///write 通过这个实例写入消息并经过ChannelPipeline//writeAndFlush 通过这个实例写入并冲刷消息并经过ChannelPipeline}

JVM内存泄漏和内存溢出的原因
JVM常用监控工具解释以及使用
Redis 常见面试题(一)
ClickHouse之MaterializeMySQL引擎(十)
三种实现分布式锁的实现与区别
线程池的理解以及使用
号外!号外!
最近面试BAT,整理一份面试资料,覆盖了Java核心技术、JVM、Java并发、SSM、微服务、数据库、数据结构等等。想获取吗?如果你想提升自己,并且想和优秀的人一起进步,感兴趣的朋友,可以在扫码关注下方公众号。资料在公众号里静静的躺着呢。。。

一键四连,你的offer也四连
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
本文作者:Java技术债务
原文链接:https://www.cuizb.top/myblog/article/1645111323
版权声明: 本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY 3.0 CN协议进行许可。转载请署名作者且注明文章出处。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有