作者:乐橙味_367 | 来源:互联网 | 2024-10-19 11:15
关于内核中的jiffies变量,可通过下图解释。
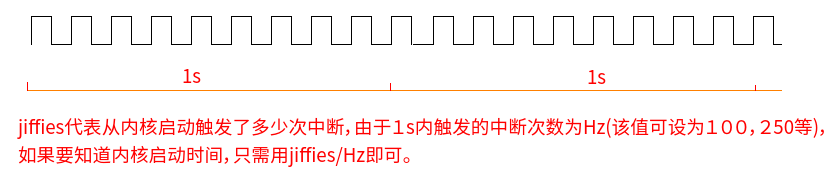
在内核中很多函数的参数都是都是以jiffies为单位的,如定时器中mod_timer(&timer, jiffies + 2*HZ);
jiffies代表当前发生中断的次数,2*Hz代表发生了发生了2*Hz次中断,那jiffies+2Hz就是未来时间点的中断次数,转换成时间就是2s后的时间点。
还有很多表示时间的用jiffies为单位的函数,如
/*** mod_timer - modify a timer's timeout* @timer: the timer to be modified* @expires: new timeout in jiffies** mod_timer() is a more efficient way to update the expire field of an* active timer (if the timer is inactive it will be activated)** mod_timer(timer, expires) is equivalent to:** del_timer(timer); timer->expires = expires; add_timer(timer);** Note that if there are multiple unserialized concurrent users of the* same timer, then mod_timer() is the only safe way to modify the timeout,* since add_timer() cannot modify an already running timer.** The function returns whether it has modified a pending timer or not.* (ie. mod_timer() of an inactive timer returns 0, mod_timer() of an* active timer returns 1.)*/
int mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires)
{expires = apply_slack(timer, expires);/** This is a common optimization triggered by the* networking code - if the timer is re-modified* to be the same thing then just return:*/if (timer_pending(timer) && timer->expires == expires)return 1;return __mod_timer(timer, expires, false, TIMER_NOT_PINNED);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mod_timer);
/*** wait_event_interruptible_timeout - sleep until a condition gets true or a timeout elapses* @wq: the waitqueue to wait on* @condition: a C expression for the event to wait for* @timeout: timeout, in jiffies** The process is put to sleep (TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE) until the* @condition evaluates to true or a signal is received.* The @condition is checked each time the waitqueue @wq is woken up.** wake_up() has to be called after changing any variable that could* change the result of the wait condition.** Returns:* 0 if the @timeout elapsed, -%ERESTARTSYS if it was interrupted by* a signal, or the remaining jiffies (at least 1) if the @condition* evaluated to %true before the @timeout elapsed.*/
#define wait_event_interruptible_timeout(wq, condition, timeout) \
({ \long __ret = timeout; \if (!___wait_cond_timeout(condition)) \__ret = __wait_event_interruptible_timeout(wq, \condition, timeout); \__ret; \
})
/*** schedule_delayed_work - put work task in global workqueue after delay* @dwork: job to be done* @delay: number of jiffies to wait or 0 for immediate execution** After waiting for a given time this puts a job in the kernel-global* workqueue.*/
static inline bool schedule_delayed_work(struct delayed_work *dwork,unsigned long delay)
当然,也有相应的函数将我们常用的时间如ms转化成jiffies的,如msecs_to_jiffies
unsigned long msecs_to_jiffies(const unsigned int m)
{/** Negative value, means infinite timeout:*/if ((int)m <0)return MAX_JIFFY_OFFSET;#if HZ <&#61; MSEC_PER_SEC && !(MSEC_PER_SEC % HZ)/** HZ is equal to or smaller than 1000, and 1000 is a nice* round multiple of HZ, divide with the factor between them,* but round upwards:*/return (m &#43; (MSEC_PER_SEC / HZ) - 1) / (MSEC_PER_SEC / HZ);
#elif HZ > MSEC_PER_SEC && !(HZ % MSEC_PER_SEC)/** HZ is larger than 1000, and HZ is a nice round multiple of* 1000 - simply multiply with the factor between them.** But first make sure the multiplication result cannot* overflow:*/if (m > jiffies_to_msecs(MAX_JIFFY_OFFSET))return MAX_JIFFY_OFFSET;return m * (HZ / MSEC_PER_SEC);
#else/** Generic case - multiply, round and divide. But first* check that if we are doing a net multiplication, that* we wouldn&#39;t overflow:*/if (HZ > MSEC_PER_SEC && m > jiffies_to_msecs(MAX_JIFFY_OFFSET))return MAX_JIFFY_OFFSET;return (MSEC_TO_HZ_MUL32 * m &#43; MSEC_TO_HZ_ADJ32)>> MSEC_TO_HZ_SHR32;
#endif
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(msecs_to_jiffies);