从视频中学得:
集合排序需要注意两点:
(1)传入对象要自己能排序(自己提供排序方法);
(2)要使用排序类
下面两个类:
1、自己定义的类
package com.collection.test1;
public class UserModule1 implements Comparable{
// 定义一些属性
private String userId, name;
private int age;
public String getUserId() {
return userId;
}
public void setUserId(String userId) {
this.userId = userId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
//重写hashCode和equals,不用每个都比较,一般只比较userId就行了
@Override
public int hashCode() {
System.out.println("call hashCode...");
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((userId == null) ? 0 : userId.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
System.out.println("call equals...");
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
UserModule1 other = (UserModule1) obj;
if (userId == null) {
if (other.userId != null)
return false;
} else if (!userId.equals(other.userId))
return false;
return true;
}
//覆盖toString
@Override
public String toString(){
return "userId=="+userId+",age=="+age+",name=="+name;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("call compareTo");
//1、对象强制造型
UserModule1 us1= (UserModule1)o;
//2、比较
System.out.println("this.getUserId()=="+this.getUserId()+",us1.getUserId()=="+us1.getUserId());
if(this.getUserId().compareTo(us1.getUserId())>0){
System.out.println(">>>>");
return 1;
}else if(this.getUserId().compareTo(us1.getUserId())==0){
System.out.println("====");
return 0;
}else{
System.out.println("<<<");
return -1;
}
}
}
Collection类
package com.collection.test1;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class CollectionTest4 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
addMethod();
}
private static void addMethod() {
//Collection col &#61; new ArrayList();
Collection col &#61; new TreeSet();
//Collection col &#61; new HashSet();
UserModule1 user1 &#61; new UserModule1();
user1.setAge(1);
user1.setName("suus");
user1.setUserId("1");
System.out.println("call set11");
// 调用add&#xff0c;就会调用hashCode
col.add(user1);
UserModule1 user2 &#61; new UserModule1();
user2.setAge(2);
user2.setName("suus2");
user2.setUserId("5");
System.out.println("call set22");
col.add(user2);
UserModule1 user3 &#61; new UserModule1();
user3.setAge(3);
user3.setName("suus3");
user3.setUserId("6");
System.out.println("call set33");
col.add(user3);
// 2enum,Iterator是一个接口&#xff0c;不能直接new&#xff0c;
Iterator it &#61; col.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
// 得到的it是Object类型的
UserModule1 a &#61; (UserModule1) it.next();
// 如果要想打印自己定义的类的各个对象&#xff0c;必须要重写toString方法。打印对象的时候&#xff0c;调用toString方法
System.out.println("a&#61;&#61;" &#43; a);
}
}
}
如果UserModule类不实现Comparable接口的话&#xff0c;在CollectionTest4 中直接用TreeSet&#xff0c;运行结果会出错&#xff1a;
如下&#xff1a;
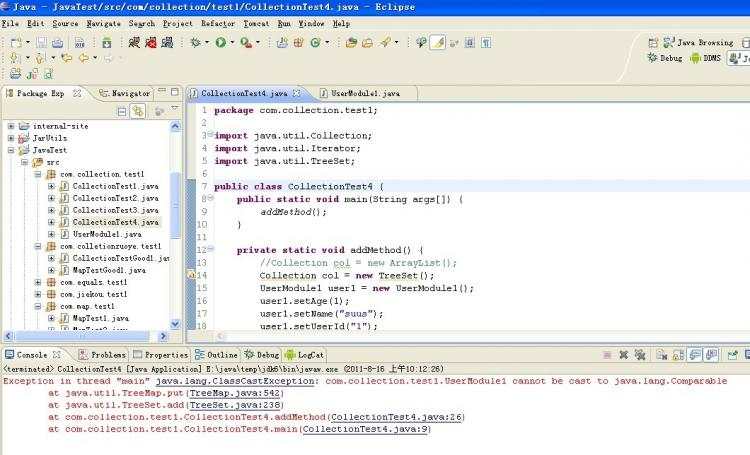
要想用TreeSet&#xff0c;UserModule必须提供比较的方法&#xff0c;所以必须implements Comparable。
注意&#xff1a;
&#xff08;1&#xff09;对于在UserModule中重写的equals方法和hashCode方法&#xff0c;当在Collection4中&#xff0c;new HashSet的时候&#xff0c;才需要重写&#xff0c;new其他的子类的时候&#xff0c;不需要重写&#xff01;&#xff01;
&#xff08;2&#xff09;要想能打印出对象的各个属性值&#xff0c;必须要重写toString方法&#xff0c;对new任何子类都是如此。
代码如上贴的时候&#xff0c;运行结果为&#xff1a;
call set11
call set22
call compareTo
this.getUserId()&#61;&#61;5,us1.getUserId()&#61;&#61;1
>>>>
call set33
call compareTo
this.getUserId()&#61;&#61;6,us1.getUserId()&#61;&#61;1
>>>>
call compareTo
this.getUserId()&#61;&#61;6,us1.getUserId()&#61;&#61;5
>>>>
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;1,age&#61;&#61;1&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;5,age&#61;&#61;2&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus2
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;6,age&#61;&#61;3&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus3
要想实现倒序排列&#xff0c;在返回1 的时候返回-1&#xff0c;在返回-1的地方返回1即可。
如果把上面的new TreeSet改成 new HashSet&#xff0c;运行结果如下&#xff1a;
call set11
call hashCode...
call set22
call hashCode...
call set33
call hashCode...
call set44
call hashCode...
call set5
call hashCode...
call set56
call hashCode...
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;6,age&#61;&#61;2&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus2
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;5,age&#61;&#61;3&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus3
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;2,age&#61;&#61;4&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus4
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;1,age&#61;&#61;1&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;4,age&#61;&#61;6&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus6
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;3,age&#61;&#61;5&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus5
与加入顺序无关
如果改成new ArrayList&#xff0c;运行结果如下&#xff1a;
call set11
call set22
call set33
call set44
call set5
call set56
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;1,age&#61;&#61;1&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;6,age&#61;&#61;2&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus2
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;5,age&#61;&#61;3&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus3
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;2,age&#61;&#61;4&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus4
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;3,age&#61;&#61;5&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus5
a&#61;&#61;userId&#61;&#61;4,age&#61;&#61;6&#xff0c;name&#61;&#61;suus6
打印出来的元素顺序与加入顺序相同





 京公网安备 11010802041100号
京公网安备 11010802041100号