API注释:Object (Java SE 15 & JDK 15) (oracle.com)
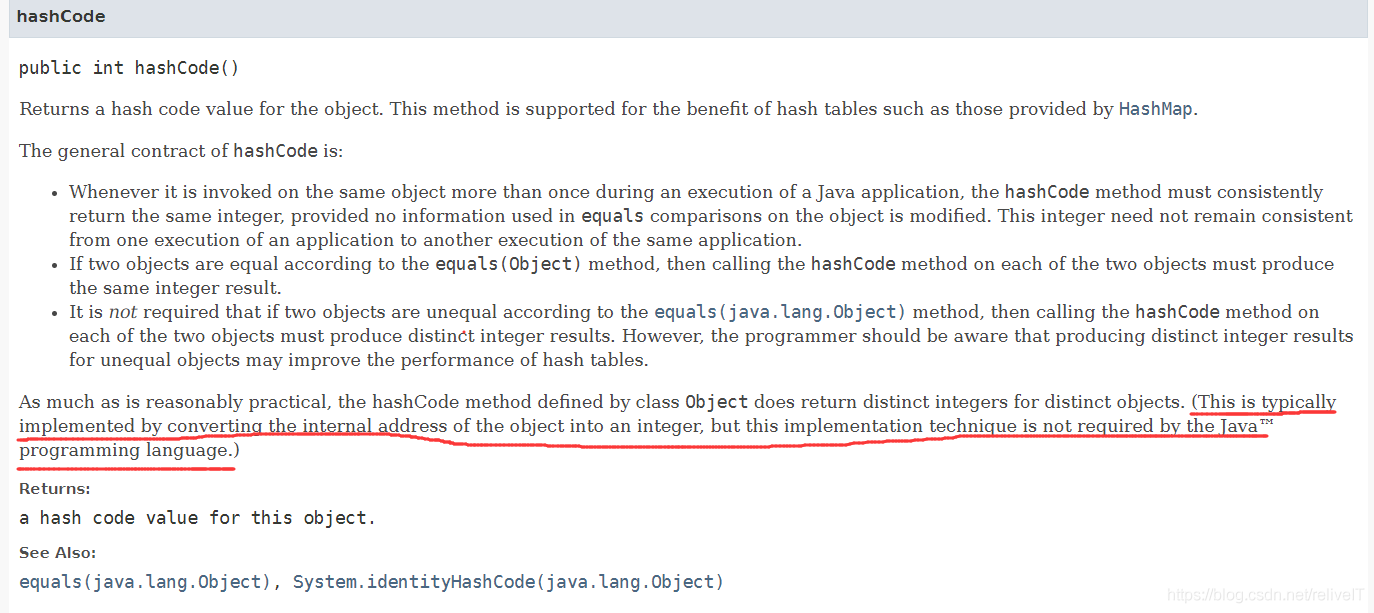
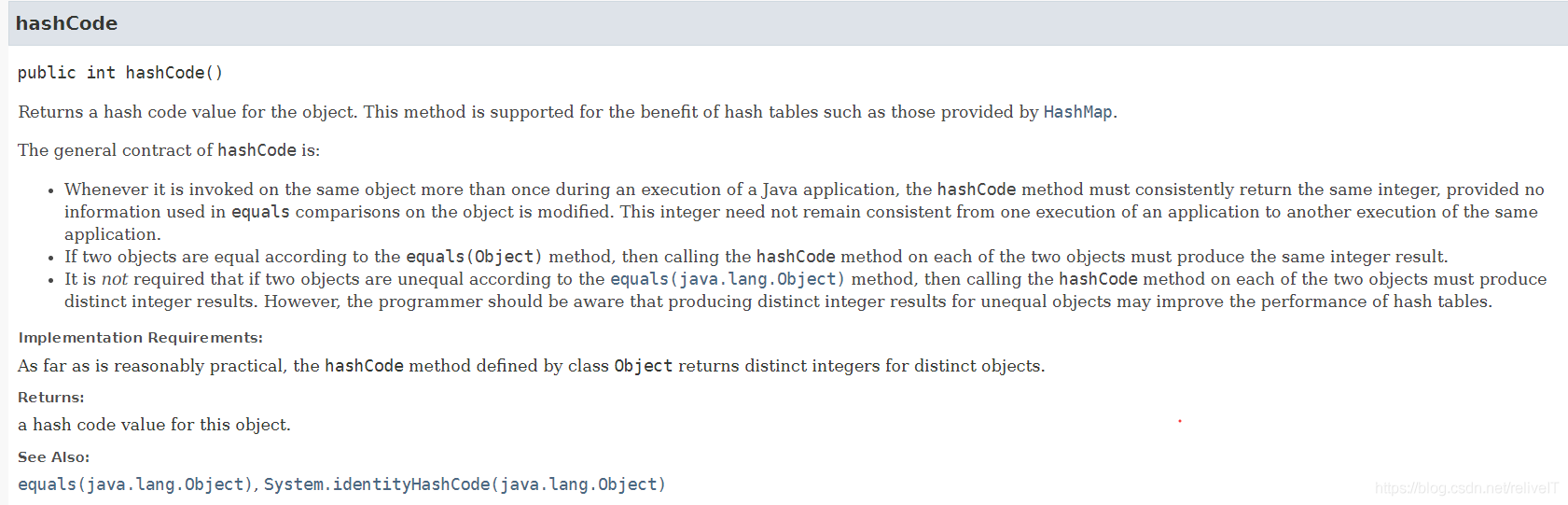
Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by
HashMap.The general contract of
hashCodeis:
- Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during an execution of a Java application, the
hashCodemethod must consistently return the same integer, provided no information used inequalscomparisons on the object is modified. This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an application to another execution of the same application.- If two objects are equal according to the
equals(Object)method, then calling thehashCodemethod on each of the two objects must produce the same integer result.- It is not required that if two objects are unequal according to the
equals(java.lang.Object)method, then calling thehashCodemethod on each of the two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables.
hashCode方法的返回值是一个int类型的哈希值,在J2SE集合框架那里一定会提到hashCode和equals方法的改写原则:
Object.hashCode()方法是一个native方法,在不同版本的API documentation中,注释文档有些许差异:

JDK8 API documentation:
This is typically implemented by converting the internal address of the object into an integer, but this implementation technique is not required by the Java™ programming language.
JDK9~12 API documentation:
The hashCode may or may not be implemented as some function of an object's memory address at some point in time.
 JDK15 API documentation:
JDK15 API documentation:
根据该方法不同版本的注释差异有:
这摸棱两可的说法,简直了。
对于Java程序员来说,虽然只需要知道这两个方法的改写原则就行,但是我们想了解的内容不止于此。
question:
接下来,我们去看看hotspot的源码。
早期JVM版本(例如JDK8),Object.hashCode()方法在Object.c文件中声明,JDK15已经改到了jvm.h头文件中声明,本文也是基于JDK15的源码来作探究。
jdk/jvm.h at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub
/*************************************************************************PART 1: Functions for Native Libraries************************************************************************/
/** java.lang.Object*/
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
JVM_IHashCode(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj);JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
JVM_MonitorWait(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj, jlong ms);JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
JVM_MonitorNotify(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj);JNIEXPORT void JNICALL
JVM_MonitorNotifyAll(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj);JNIEXPORT jobject JNICALL
JVM_Clone(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj);
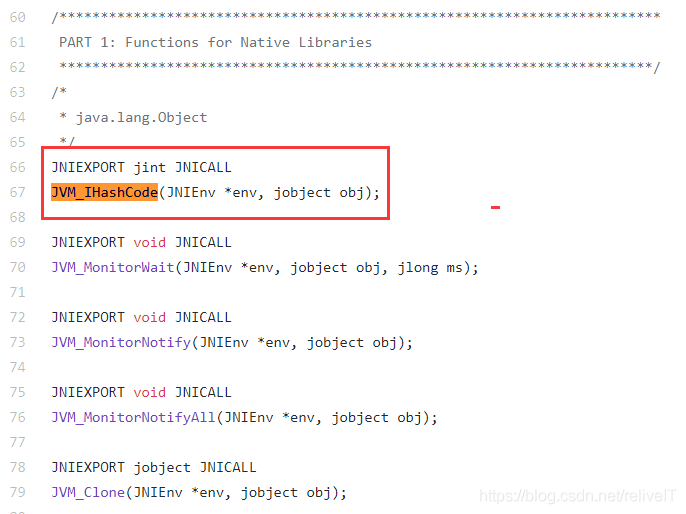
Object.hashCode()方法在jvm.cpp中实现:
jdk/jvm.cpp at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub
JVM_ENTRY(jint, JVM_IHashCode(JNIEnv* env, jobject handle))// as implemented in the classic virtual machine; return 0 if object is NULLreturn handle == NULL ? 0 : ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (THREAD, JNIHandles::resolve_non_null(handle)) ;
JVM_END

ObjectSynchronizer类在synchronizer.hpp文件中声明,在synchronizer.cpp中实现:
jdk/synchronizer.cpp at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub
intptr_t ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode(Thread* current, oop obj) {while (true) {ObjectMonitor* mOnitor= NULL;markWord temp, test;intptr_t hash;markWord mark = read_stable_mark(obj);if (mark.is_neutral()) { // if this is a normal headerhash = mark.hash();if (hash != 0) { // if it has a hash, just return itreturn hash;}hash = get_next_hash(current, obj); // get a new hashtemp = mark.copy_set_hash(hash); // merge the hash into header// try to install the hashtest = obj->cas_set_mark(temp, mark);if (test == mark) { // if the hash was installed, return itreturn hash;}// Failed to install the hash. It could be that another thread// installed the hash just before our attempt or inflation has// occurred or... so we fall thru to inflate the monitor for// stability and then install the hash.} else if (mark.has_monitor()) {mOnitor= mark.monitor();temp = monitor->header();assert(temp.is_neutral(), "invariant: header=" INTPTR_FORMAT, temp.value());hash = temp.hash();if (hash != 0) {// It has a hash.// Separate load of dmw/header above from the loads in// is_being_async_deflated().// dmw/header and _contentions may get written by different threads.// Make sure to observe them in the same order when having several observers.OrderAccess::loadload_for_IRIW();if (monitor->is_being_async_deflated()) {// But we can't safely use the hash if we detect that async// deflation has occurred. So we attempt to restore the// header/dmw to the object's header so that we only retry// once if the deflater thread happens to be slow.monitor->install_displaced_markword_in_object(obj);continue;}return hash;}// Fall thru so we only have one place that installs the hash in// the ObjectMonitor.} else if (current->is_lock_owned((address)mark.locker())) {// This is a stack lock owned by the calling thread so fetch the// displaced markWord from the BasicLock on the stack.temp = mark.displaced_mark_helper();assert(temp.is_neutral(), "invariant: header=" INTPTR_FORMAT, temp.value());hash = temp.hash();if (hash != 0) { // if it has a hash, just return itreturn hash;}// WARNING:// The displaced header in the BasicLock on a thread's stack// is strictly immutable. It CANNOT be changed in ANY cases.// So we have to inflate the stack lock into an ObjectMonitor// even if the current thread owns the lock. The BasicLock on// a thread's stack can be asynchronously read by other threads// during an inflate() call so any change to that stack memory// may not propagate to other threads correctly.}// Inflate the monitor to set the hash.// An async deflation can race after the inflate() call and before we// can update the ObjectMonitor's header with the hash value below.mOnitor= inflate(current, obj, inflate_cause_hash_code);// Load ObjectMonitor's header/dmw field and see if it has a hash.mark = monitor->header();assert(mark.is_neutral(), "invariant: header=" INTPTR_FORMAT, mark.value());hash = mark.hash();if (hash == 0) { // if it does not have a hashhash = get_next_hash(current, obj); // get a new hashtemp = mark.copy_set_hash(hash) ; // merge the hash into headerassert(temp.is_neutral(), "invariant: header=" INTPTR_FORMAT, temp.value());uintptr_t v = Atomic::cmpxchg((volatile uintptr_t*)monitor->header_addr(), mark.value(), temp.value());test = markWord(v);if (test != mark) {// The attempt to update the ObjectMonitor's header/dmw field// did not work. This can happen if another thread managed to// merge in the hash just before our cmpxchg().// If we add any new usages of the header/dmw field, this code// will need to be updated.hash = test.hash();assert(test.is_neutral(), "invariant: header=" INTPTR_FORMAT, test.value());assert(hash != 0, "should only have lost the race to a thread that set a non-zero hash");}if (monitor->is_being_async_deflated()) {// If we detect that async deflation has occurred, then we// attempt to restore the header/dmw to the object's header// so that we only retry once if the deflater thread happens// to be slow.monitor->install_displaced_markword_in_object(obj);continue;}}// We finally get the hash.return hash;}
}
因为JDK15中已经废弃掉了偏向锁(见JEP 374: Disable and Deprecate Biased Locking,JDK 15 features 374),所以相比较之前的实现,在ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode方法中已经移除了偏向锁的判断,之前的版本在本文附注中贴出。
ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode方法中有普通对象、重量级锁、轻量级锁几种情况,我们主要选取普通对象计算并保存哈希值的case来做研究,ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode方法逻辑是这样的:
上述hotspot对hashCode()方法的实现中标红部分有两个关键点:mark word和get_next_hash(thread, obj)方法。
关于mark word,在《Java对象的对齐规则》一文4.1章节谈对象头时,其源码和结构已经分析过了,如果你不太熟悉,可以先看看这一部分再往下阅读。
在32bit机器上,mark word中有25bit用于保存哈希值,64bit机器上,有31bit用于保存哈希值,源码注释中给的结构是这样的:
// 32 bits:
// --------
// hash:25 ------------>| age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object)
// JavaThread*:23 epoch:2 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object)
// size:32 ------------------------------------------>| (CMS free block)
// PromotedObject*:29 ---------->| promo_bits:3 ----->| (CMS promoted object)
//
// 64 bits:
// --------
// unused:25 hash:31 -->| unused:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (normal object)
// JavaThread*:54 epoch:2 unused:1 age:4 biased_lock:1 lock:2 (biased object)
// PromotedObject*:61 --------------------->| promo_bits:3 ----->| (CMS promoted object)
// size:64 ----------------------------------------------------->| (CMS free block)//
// - the two lock bits are used to describe three states: locked/unlocked and monitor.
//
// [ptr | 00] locked ptr points to real header on stack
// [header | 0 | 01] unlocked regular object header
// [ptr | 10] monitor inflated lock (header is wapped out)
// [ptr | 11] marked used by markSweep to mark an object
所以上文第一个问题Object.hashCode()方法怎么保持哈希值不变就有了答案:
所以暂且不论get_next_hash(thread, obj)方法计算对象哈希值是否基于对象的内存地址,即便是基于对象内存地址,GC后对象移动,但是保存在其对象头的mark word中的哈希值还是第一次调用hashCode()方法得到得到哈希值。
我们在后续第三节测试验证的时候,会通过jol工具观察整个过程来做验证,jol工具(Java object layout)是openjdk开源的一款查看Java对象内存布局的工具,在《Java对象的对齐规则》一文中也有介绍。
static inline intptr_t get_next_hash(Thread* current, oop obj) {intptr_t value = 0;if (hashCode == 0) {// This form uses global Park-Miller RNG.// On MP system we'll have lots of RW access to a global, so the// mechanism induces lots of coherency traffic.value = os::random();} else if (hashCode == 1) {// This variation has the property of being stable (idempotent)// between STW operations. This can be useful in some of the 1-0// synchronization schemes.intptr_t addr_bits = cast_from_oop
}
get_next_hash(thread, obj)方法中有五种哈希值计算方式:
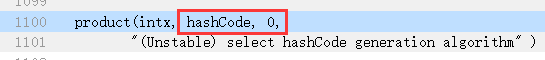
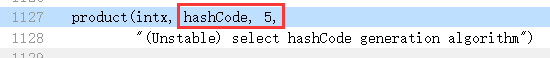
到底用的哪一种计算方式,和参数hashCode有关系,这个参数在globals.hpp中有默认配置,你可以通过虚拟机启动参数-XX:hashCode=n来做修改。

对于Marsaglia异或移位方案,线程状态是指hotspot中Thread类的四个属性_hashStateW、_hashStateX、_hashStateY、_hashStateZ,这四个属性在Thread.hpp文件中定义:
jdk/thread.hpp at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub

在Thread.cpp文件中赋值:
jdk/thread.cpp at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub

最后在ObjectSynchronizer类中获取通过Marsaglia异或移位方案计算出对象默认哈希值。
所以,从openjdk的多个版本来看,Object.hashCode()方法的默认实现并没有采用对象的内存地址来计算。
所以第一和第二个问题,就不需要再纠结了。
在hotspot中,java.lang.System.identityHashCode(Object)的实现是直接转调JVM_IHashCode,也就是说System.identityHashCode的实现就是Object.hashCode在hotspot中的实现。
jdk/System.c at master · openjdk/jdk · GitHub
JNIEXPORT jint JNICALL
Java_java_lang_System_identityHashCode(JNIEnv *env, jobject this, jobject x)
{return JVM_IHashCode(env, x);
}

所以,有如下几种情形
这里需要用到openjdk的开源工具jol(Java object layout),查看Java对象内存布局的工具,工具在《Java对象的对齐规则》一文中已经介绍,如果你不熟悉,可以先看看这篇文章。
Dummy类用于创建占位对象,用来创建4M的byte数组,用于触发GC。
/*** 占位资源,4M的字节数组,用于测试用触发GC操作* @author 王大锤* @date 2021年7月18日*/
public class Dummy {@SuppressWarnings("unused")private byte[] dummy = new byte[4 * 1024 * 1024];
}
jvm的启动参数:
-Xmx20m -Xmx20m -XX:+PrintGCDetails
测试代码,其中要用到jol工具的org.openjdk.jol.vm.VM类:
public static void main(String[] args) {Object object = new Object();System.out.println("GC前:");addressOf(object);new Dummy();new Dummy();new Dummy();System.gc();System.out.println("GC后:");addressOf(object);}private static
测试结果,为了方便阅读,-XX:+PrintGCDetails打印的GC信息省略掉了:
GC前:
java.lang.Object@33f88ab hashCode is: 54495403, address is: 34359268032GC后:
java.lang.Object@33f88ab hashCode is: 54495403, address is: 34200357760
gc前后对象默认的哈希值都是54495403,gc前对象的内存地址34359268032,gc后对象的内存地址变为了34200357760。
从上面的分析可知,默认哈希值保存到了对象头的mark word中,所以虽然GC移动了对象在内存中的位置,但是其默认哈希值并未改变。
至于将哈希值保存在对象头mark word中,请参看下一个测试。
测试代码,其中要用到jol工具的org.openjdk.jol.info.ClassLayout类:
Object object = new Object();System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(object).toPrintable());System.out.println(object.hashCode());System.out.println(ClassLayout.parseInstance(object).toPrintable());
测试结果:
java.lang.Object object internals:
OFF SZ TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 8 (object header: mark) 0x0000000000000001 (non-biasable; age: 0)
8 4 (object header: class) 0x00002080
12 4 (object alignment gap)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total2116908859
java.lang.Object object internals:
OFF SZ TYPE DESCRIPTION VALUE
0 8 (object header: mark) 0x0000007e2d773b01 (hash: 0x7e2d773b; age: 0)
8 4 (object header: class) 0x00002080
12 4 (object alignment gap)
Instance size: 16 bytes
Space losses: 0 bytes internal + 4 bytes external = 4 bytes total
结果分析:
本机环境64bit widnows,开启压缩指针,所以对象头中前8字节是mark word,接着4字节是元数据指针_compressed_klass,最后4字节是Java默认的对象间8字节对齐所需要填补的对齐填充。
其中没调用hashCode方法前,mark word中对应的比特位值为0,调用之后,计算出的默认哈希值会填充到mark word对应的比特位,见下图:

openjdk7中ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode源码,未移除偏向锁:
intptr_t ObjectSynchronizer::FastHashCode (Thread * Self, oop obj) {if (UseBiasedLocking) {// NOTE: many places throughout the JVM do not expect a safepoint// to be taken here, in particular most operations on perm gen// objects. However, we only ever bias Java instances and all of// the call sites of identity_hash that might revoke biases have// been checked to make sure they can handle a safepoint. The// added check of the bias pattern is to avoid useless calls to// thread-local storage.if (obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern()) {// Box and unbox the raw reference just in case we cause a STW safepoint.Handle hobj (Self, obj) ;// Relaxing assertion for bug 6320749.assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(),"biases should not be seen by VM thread here");BiasedLocking::revoke_and_rebias(hobj, false, JavaThread::current());obj = hobj() ;assert(!obj->mark()->has_bias_pattern(), "biases should be revoked by now");}}// hashCode() is a heap mutator ...// Relaxing assertion for bug 6320749.assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||!SafepointSynchronize::is_at_safepoint(), "invariant") ;assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||Self->is_Java_thread() , "invariant") ;assert (Universe::verify_in_progress() ||((JavaThread *)Self)->thread_state() != _thread_blocked, "invariant") ;ObjectMonitor* mOnitor= NULL;markOop temp, test;intptr_t hash;markOop mark = ReadStableMark (obj);// object should remain ineligible for biased lockingassert (!mark->has_bias_pattern(), "invariant") ;if (mark->is_neutral()) {hash = mark->hash(); // this is a normal headerif (hash) { // if it has hash, just return itreturn hash;}hash = get_next_hash(Self, obj); // allocate a new hash codetemp = mark->copy_set_hash(hash); // merge the hash code into header// use (machine word version) atomic operation to install the hashtest = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(temp, obj->mark_addr(), mark);if (test == mark) {return hash;}// If atomic operation failed, we must inflate the header// into heavy weight monitor. We could add more code here// for fast path, but it does not worth the complexity.} else if (mark->has_monitor()) {mOnitor= mark->monitor();temp = monitor->header();assert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;hash = temp->hash();if (hash) {return hash;}// Skip to the following code to reduce code size} else if (Self->is_lock_owned((address)mark->locker())) {temp = mark->displaced_mark_helper(); // this is a lightweight monitor ownedassert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;hash = temp->hash(); // by current thread, check if the displacedif (hash) { // header contains hash codereturn hash;}// WARNING:// The displaced header is strictly immutable.// It can NOT be changed in ANY cases. So we have// to inflate the header into heavyweight monitor// even the current thread owns the lock. The reason// is the BasicLock (stack slot) will be asynchronously// read by other threads during the inflate() function.// Any change to stack may not propagate to other threads// correctly.}// Inflate the monitor to set hash codemOnitor= ObjectSynchronizer::inflate(Self, obj);// Load displaced header and check it has hash codemark = monitor->header();assert (mark->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;hash = mark->hash();if (hash == 0) {hash = get_next_hash(Self, obj);temp = mark->copy_set_hash(hash); // merge hash code into headerassert (temp->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;test = (markOop) Atomic::cmpxchg_ptr(temp, monitor, mark);if (test != mark) {// The only update to the header in the monitor (outside GC)// is install the hash code. If someone add new usage of// displaced header, please update this codehash = test->hash();assert (test->is_neutral(), "invariant") ;assert (hash != 0, "Trivial unexpected object/monitor header usage.");}}// We finally get the hashreturn hash;
}
附注:本文如有错漏,烦请指正!

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有