点互信息
Pointwise mutual information (PMI), or point mutual information, is a measure of association used in information theory andstatistics.
The PMI of a pair of outcomes x and y belonging to discrete random variables X and Y quantifies the discrepancy between the probability of their coincidence given their joint distribution and their individual distributions, assuming independence.
来自
The mutual information (MI) of the random variables X and Y is the expected value of the PMI over all possible outcomes (w.r.t. the joint distribution
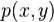
).
来自
http://www.eecis.udel.edu/~trnka/CISC889-11S/lectures/philip-pmi.pdf
Information-theory approach to find
collocations
– Measure of how much one word tells us about the
other. How much information we gain
– Can be negative or positive
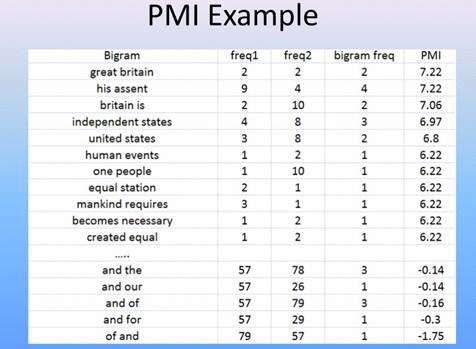
Problems with PMI
• Bad with sparse data
– Suppose some words only occur once, but appear
together
– Get very high score PMI score
– Consider our word clouds. High PMI score might
not necessarily indicate importance of bigram
来自
点互信息由互信息而来
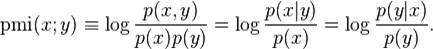
来自
Finally,
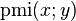
will increase if
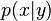
is fixed but
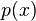
decreases.
这就是一个不好的地方 如果联系紧密 必然一同出现 p(x|y) 那么取决于p(x)的值大小 越不常见的x 值越大 假设 p(y|x)=1 完全相同共现 就就取决于变量的出现频度了 只出现一次分数最高 偏爱稀有 低频情况
Bad with word dependence
– Suppose two words are perfectly dependent on
eachother
– Whenever one occurs, the other occurs
– I(x, y) = log (1 / P(y))
– So the rarer the word is, the higher the PMI is
– High PMI score doesn't mean high word
dependence (could just mean rarer words)
– Threshold on word frequencies
来自
可以看做局部一个点的互信息
考虑互信息
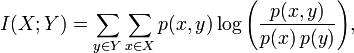
来自
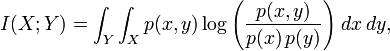
来自
It can take positive or negative values, but is zero if X and Y areindependent. PMI maximizes when X and Y are perfectly associated, yielding the following bounds:
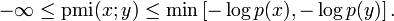
来自
例子
| x | y | p(x, y) |
| 0 | 0 | 0.1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0.7 |
| 1 | 0 | 0.15 |
| 1 | 1 | 0.05 |
Using this table we can marginalize to get the following additional table for the individual distributions:
|
| p(x) | p(y) |
| 0 | .8 | 0.25 |
| 1 | .2 | 0.75 |
With this example, we can compute four values for
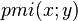
. Using base-2 logarithms:
| pmi(x=0;y=0) | −1 |
| pmi(x=0;y=1) | 0.222392421 |
| pmi(x=1;y=0) | 1.584962501 |
| pmi(x=1;y=1) | −1.584962501 |
(For reference, the mutual information
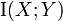
would then be 0.214170945)
来自
和互信息的相似处
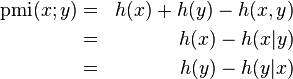
Where
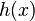
is the self-information, or
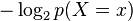
.
来自
正规化的pmi npmi
Pointwise mutual information can be normalized between [-1,+1] resulting in -1 (in the limit) for never occurring together, 0 for independence, and +1 for complete co-occurrence.
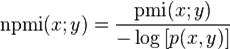
完全共现的时候 可以认为 p(x,y) = p(x)=p(y) 结合
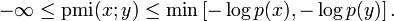
来自
Chain-rule for pmi
来自
没太明白 这个TODO
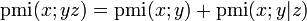
This is easily proven by:
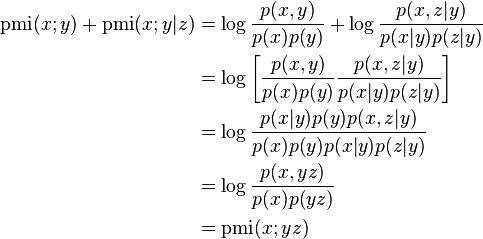
来自





 京公网安备 11010802041100号
京公网安备 11010802041100号