本教程分享了在寒武纪设备上 pytorch-mlu 中添加逐层算子的方法。
pytorch-mlu 逐层模式中算子间数据传递和存储的基本单元是 tensor。pytorch-mlu 根据 tensor 中的 device 属性值将算子分发到不同设备。以 abs() 算子为例,在 dispatch 阶段会根据 input_tensor 的设备属性值将算子调用分发到具体设备,逻辑如下图所示:
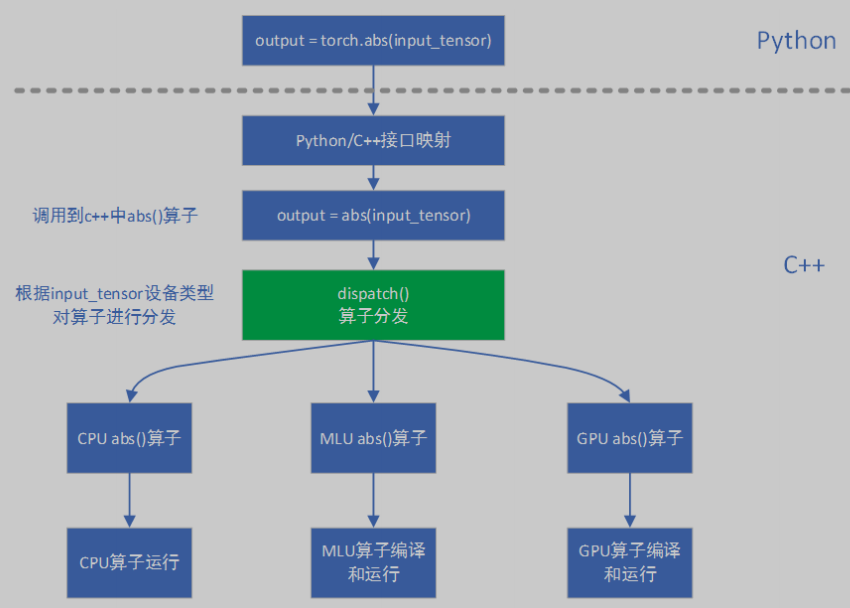
catch 通过注册添加 mlu 算子方式与 pytorch 源码解耦,下面介绍在 catch 中添加 mlu 算子的具体步骤。
在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/generated/aten_mlu_type_default.cpp 中注册算子:
.op(torch::registeroperators::options().schema("aten::add.tensor(tensor self, tensor other, *, scalar alpha=1) -> tensor") // nolint .impl_unboxedonlykernel(at::tensortypeid::mlutensorid) aliasanalysis(c10::aliasanalysiskind::from_schema))
atenmlutype 和 atenmlucustomtype 是 catch 模块中算子的入口。atenmlutype 类主要包含框架中的标准算子;而 atenmlucustomtype 类包含客制化的算子。根据算子属性选择在 atenmlutype 还是 atenmlucustomtype 中添加相应算子声明和实现。
标准算子分发
在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/aten_mlu_type.h 和 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/aten_mlu_type.cpp 中添加算子声明和实现:
aten_mlu_type.h static at::tensor add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha); aten_mlu_type.cpp at::tensor atenmlutype::add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha){ return op_dispatch(add, self, other, alpha); }
客制化算子分发
对于 mlu 特有算子,在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/aten_mlu_type.h和 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/aten_mlu_custom_type.cpp 中添加算子申明和实现:
aten_mlu_type.h static at::tensor linear(const at::tensor& input, const at::tensor& weight, const at::tensor& bias, const at::tensor& q_scale, const at::tensor& q_mode); aten_mlu_custom_type.cpp at::tensor atenmlucustomtype::linear(const at::tensor& input, const at::tensor& weight, const at::tensor& bias, const at::tensor& q_scale, const at::tensor& q_mode){ return op_dispatch(linear, input, weight, bias, q_scale, q_mode); }
从 atenmlutype 和 atenmlucustomtype 中都会通过 opmethods 下发到推理算子或训练算子。在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/op_methods.h 和 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/op_methods.cpp 中添加算子申明和实现。opmethods 中的实现部分为该算子的 cpu 实现。
op_methods.h virtual at::tensor add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha); op_methods.cpp at::tensor opmethods::add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha){ auto input_cpu = self.cpu(); auto other_cpu = other.cpu(); auto output = at::add(input_cpu, other_cpu, alpha); return output.to(at::device(at::device::type::mlu)); }
在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/cnml_ops.h 和 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/cnml_ops.cpp 中添加推理算子申明和实现。
cnml_ops.h at::tensor add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha); cnml_ops.cpp at::tensor cnmlops::add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha){ cnml_dispatch(add, cnml_add, self, other, alpha); // cnml_dispatch 宏第一个参数是该接口名,第二个参数是wrapper个名字,其余 }
wrapper 是对算子 kernel 的封装,每个算子对应一个 wrapper。这里以 add 算子为例,添加 wrapper 如下所示:
cnml_kernel.h at::tensor cnml_add(const at::tensor& input, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha); add.cpp at::tensor cnml_add(const at::tensor& input, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha_scalar){ torch_check(input.dim() >= 0 || other.dim() >= 0, "dimension not support"); at::tensor input_ = input; at::tensor other_ = other; auto alpha_data = alpha_scalar.to(); if(alpha_data != 1){ // scale_t other_ = cnml::ops::cnml_scale(other_, alpha_data, 0); } if(other_.dim() <1 && other_.device().type() == c10::devicetype::cpu){ auto other_scalar = other_.item(); return cnml_add_internal(input_, other_scalar); // 调用kernel } if(input_.dim() <1 && input_.device().type() == c10::devicetype::cpu){ auto input_scalar = input_.item(); return cnml_add_internal(other_, input_scalar); // 调用 kernel } bool broadcast = input_.sizes() != other_.sizes(); if(broadcast){ auto broadcast_size = at::infer_size(input.sizes(), other.sizes()); at::tensor broadcast1 = cnml::ops::cnml_expand(input_, broadcast_size, false); at::tensor broadcast2 = cnml::ops::cnml_expand(other_, broadcast_size, false); return cnml_add_internal(broadcast1, broadcast2); // 调用 kernel }else{ return cnml_add_internal(input_, other_); //调用 kernel } return cnml_add_internal(input_, other_); //调用 kernel }
wrapper 中通过调用 kernel 实现算子功能。示例中调用的是 cnml_add_internal。算子的具体实现主要通过调用 cnml 库的接口来完成,下面是 cnml 库的逻辑:

kernel 实现就是按照上述编程逻辑调用 cnml 库接口完成的,在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/cnml/internal/cnml_internal.h 和 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/cnml/internal/add_internal/cpp 中添加 kernel 函数的声明和实现。
cnml_internal.h at::tensor cnml_add_internal(const at::tensor& input1, const at::tensor& input2); add_internal.cpp at::tensor cnml_add_internal(const at::tensor& input1, const at::tensor& input2){ auto output = at::native::empty_like(input1); // prepare input cnml tensor auto* input1_impl = getmlutensorimpl(input1); // 获取mlutensorimpl auto input1_cnml = input1_impl->createcnmltensor( cnml_tensor, tocnmldatatype(input1.dtype())); // 类型自适应:tocnmldatatype() auto* input2_impl = getmlutensorimpl(input2); auto input2_cnml = input2_impl->createcnmltensor( cnml_tensor, tocnmldatatype(input2.dtype())); // prepare output cnml tensor auto* output_impl = getmlutensorimpl(output); auto output_cnml = output_impl->createcnmltensor( cnml_tensor, tocnmldatatype(output.dtype())); // end the execution flow if not mlu device check_mlu_device(output); // setup operator cnmlbaseop_t add_op; torch_cnml_check(cnmlcreateaddop(&add_op, input1_cnml, input2_cnml, output_cnml)); // return to jit if running mode is fuse chexk_return_to_fuse(add_op, output); // compile op torch_cnml_check(cnmlcompilebaseop(add_op, get_core_version, get_core_number)); auto queue = getcurqueue(); torch_cnml_check(cnmlcomputeaddopforward_v4(add_op, null, input1_impl->raw_mutable_data(), null, input2_impl->raw_mutable_data(), null, output_impl->raw_mutable_data(), queue, null)); syncqueue(queue); torch_cnml_check(cnmldestroybaseop(&add_op)); return output; }
对 mlu 不支持算子的处理
对于 mlu 暂不支持的操作,输入数据将会拷贝到 cpu 上,然后调用 cpu 相关操作,使其在 cpu 上运行,最后再将输出结果拷会到 mlu 上。具体实现,可以查询 op_methods.cp,该文件在 catch/torch_mlu/csrc/aten/operators/ 目录下。
op_methods.cpp at::tensor opmethods::add(const at::tensor& self, const at::tensor& other, at::scalar alpha){ auto input_cpu = self.cpu(); auto other_cpu = other.cpu(); auto output = at::add(input_cpu, other_cpu, alpha); return output.to(at::device(at::device::type::mlu)); }
对于新增的算子在执行过程中抛出异常时,如果 cpu 上没有对应的算子操作,那么该操作无法切换到 cpu 上运行;
wrapper一般以 cnml_算子名命名,kernel一般以cnml_算子名_internal命名
使用基于 python 的 unittest 模块编写算子单元测试。测试时需提供相同的参数和输入数据,分别在 mlu 和 cpu 上执行算子,对比两者的输出结果。mlu 和 cpu 计算结果可能会有差异,一般情况下两者的相对误差在 2% 以内均是可以接受的。
def test_add(self): # "tensor + tensor" mode testing for shape1, shape2 in [((1,3,224,224),(1,3,224,224)),((2,30,80),(2,30,80)),((3,20),(3,20)),((10),(10))]: input1_cpu = torch.rand(shape1, dtype=torch.float) input2_cpu = torch.rand(shape2, dtype=torch.float) input1_mlu = input1_cpu.to(xm.mlu_device()) input2_mlu = input2_cpu.to(xm.mlu_device()) # 在 cpu 上计算 output_cpu = input1_cpu + input2_cpu # 在 mlu 上计算 output_mlu = input1_mlu + input2_mlu # 计算 mlu 的误差,并确保相对误差在 2% 以内 self.asserttensorsequal(output_cpu, output_mlu.cpu(), 0.02, use_mse=true)
以上分享了在寒武纪设备 pytorch-mlu 中添加逐层算子的方法,并以 add() 算子为例进行了示例编写,希望我的分享会对你的学习有一点帮助。
到此这篇关于pytorch-mlu 实现添加逐层算子方法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pytorch内容请搜索<编程笔记>以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持<编程笔记>!
需要了解更多python教程分享Pytorch-mlu 实现添加逐层算子方法详解,都可以关注python教程分享栏目&#8212;编程笔记

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有