View仿华为圆形加载进度条效果图
实现思路
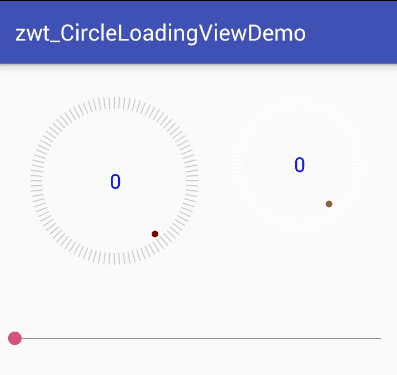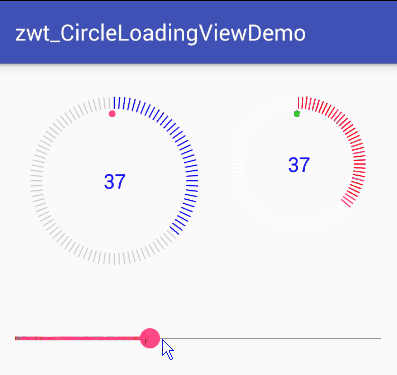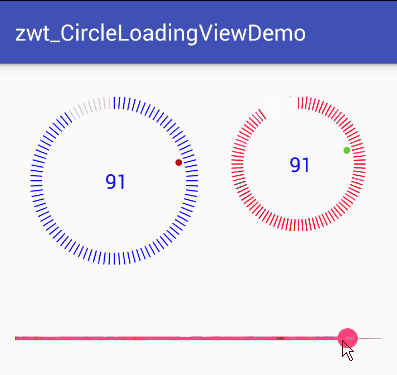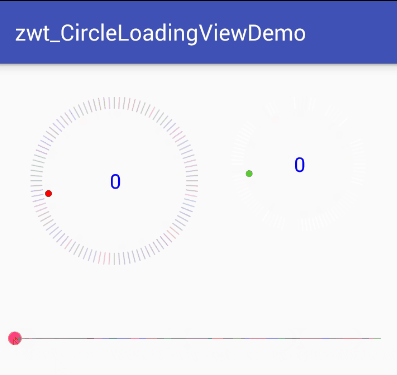
可以看出该View可分为三个部分来实现
最外围的圆,该部分需要区分进度圆和底部的刻度圆,进度部分的刻度需要和底色刻度区分开来
中间显示的文字进度,需要让文字在View中居中显示
旋转的小圆点,小圆点需要模拟小球下落运动时的加速度效果,开始下落的时候慢,到最底部时最快,上来时速度再逐渐减慢
具体实现
先具体细分讲解,博客最后面给出全部源码
(1)首先为View创建自定义的xml属性
在工程的values目录下新建attrs.xml文件
各个属性的作用:
indexColor:进度圆的颜色
baseColor:刻度圆底色
dotColor:小圆点颜色
textSize:文字大小
textColor:文字颜色
(2)新建CircleLoadingView类继承View类,重写它的三个构造方法,获取用户设置的属性,同时指定默认值
public CircleLoadingView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CircleLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CircleLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// 获取用户配置属性
TypedArray tya = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleLoading);
baseColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_baseColor, Color.LTGRAY);
indexColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_indexColor, Color.BLUE);
textColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_textColor, Color.BLUE);
dotColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_dotColor, Color.RED);
textSize = tya.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CircleLoading_textSize, 36);
tya.recycle();
initUI();
}
我们从View绘制的第一步开始
(3)测量onMeasure,首先需要测量出View的宽和高,并指定View在wrap_content时的最小范围,对于View绘制流程还不熟悉的同学,可以先去了解下具体的绘制流程
浅谈Android View绘制三大流程探索及常见问题
重写onMeasure方法,其中我们要考虑当View的宽高被指定为wrap_content时的情况,如果我们不对wrap_content的情况进行处理,那么当使用者指定View的宽高为wrap_content时将无法正常显示出View
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int myWidthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int myWidthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int myHeightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int myHeightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 获取宽
if (myWidthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// match_parent/精确值
mWidth = myWidthSpecSize;
} else {
// wrap_content
mWidth = DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 120);
}
// 获取高
if (myHeightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// match_parent/精确值
mHeight = myHeightSpecSize;
} else {
// wrap_content
mHeight = DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 120);
}
// 设置该view的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}
MeasureSpec的状态分为三种EXACTLY、AT_MOST、UNSPECIFIED,这里只要单独指定非精确值EXACTLY之外的情况就好了。
本文中使用到的DensityUtil类,是为了将dp转换为px来使用,以便适配不同的屏幕显示效果
public static int dip2px(Context context, float dpValue) {
final float scale = context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density;
return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f);
}
(4)重写onDraw,绘制需要显示的内容
因为做的是单纯的View而不是ViewGroup,内部没有子控件需要确定位置,所以可直接跳过onLayout方法,直接开始对View进行绘制
分为三个部分绘制,绘制刻度圆,绘制文字值,绘制旋转小圆点
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
drawArcScale(canvas);
drawTextValue(canvas);
drawRotateDot(canvas);
}
绘制刻度圆
先画一个小竖线,通过canvas.rotate()方法每次旋转3.6度(总共360度,用100/360=3.6)得到一个刻度为100的圆,然后通过progress参数,得到要显示的进度数,并把小于progress的刻度变成进度圆的颜色
/**
* 画刻度
*/
private void drawArcScale(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
for (int i = 0; i <100; i++) {
if (progress > i) {
mScalePaint.setColor(indexColor);
} else {
mScalePaint.setColor(baseColor);
}
canvas.drawLine(mWidth / 2, 0, mHeight / 2, DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 10), mScalePaint);
// 旋转的度数 = 100 / 360
canvas.rotate(3.6f, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
}
canvas.restore();
}
绘制中间文字
文字绘制的坐标是以文字的左下角开始绘制的,所以需要先通过把文字装载到一个矩形Rect,通过画笔的getTextBounds方法取得字符串的长度和宽度,通过动态计算,来使文字居中显示
/**
* 画内部数值
*/
private void drawTextValue(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
String showValue = String.valueOf(progress);
Rect textBound = new Rect();
mTextPaint.getTextBounds(showValue, 0, showValue.length(), textBound); // 获取文字的矩形范围
float textWidth = textBound.right - textBound.left; // 获得文字宽
float textHeight = textBound.bottom - textBound.top; // 获得文字高
canvas.drawText(showValue, mWidth / 2 - textWidth / 2, mHeight / 2 + textHeight / 2, mTextPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
绘制旋转小圆点
这个小圆点就是简单的绘制一个填充的圆形就好
/**
* 画旋转小圆点
*/
private void drawRotateDot(final Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(mDotProgress * 3.6f, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 10) + DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 5), DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 3), mDotPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
让它自己动起来可以通过两种方式,一种是开一个线程,在线程中改变mDotProgress的数值,并通过postInvalidate方法跨线程刷新View的显示效果
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
mDotProgress++;
if (mDotProgress == 100) {
mDotProgress = 0;
}
postInvalidate();
try {
Thread.sleep(50);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
开线程的方式不推荐使用,这是没必要的开销,而且线程不好控制,要实现让小圆点在运行过程中开始和结束时慢,运动到中间时加快这种效果不好实现,所以最好的方式是使用属性动画,需要让小圆点动起来时,调用以下方法就好了
/**
* 启动小圆点旋转动画
*/
public void startDotAnimator() {
animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 100);
animator.setDuration(1500);
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART);
animator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// 设置小圆点的进度,并通知界面重绘
mDotProgress = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
animator.start();
}
在属性动画中可以通过setInterpolator方法指定不同的插值器,这里要模拟小球掉下来的重力效果,所以需要使用AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator插值类,该类的效果就是在动画开始时和结束时变慢,中间加快
(5)设置当前进度值
对外提供一个方法,用来更新当前圆的进度
/**
* 设置进度
*/
public void setProgress(int progress) {
this.progress = progress;
invalidate();
}
通过外部调用setProgress方法就可以跟更新当前圆的进度了
源码
/**
* 仿华为圆形加载进度条
* Created by zhuwentao on 2017-08-19.
*/
public class CircleLoadingView extends View {
private Context mContext;
// 刻度画笔
private Paint mScalePaint;
// 小原点画笔
private Paint mDotPaint;
// 文字画笔
private Paint mTextPaint;
// 当前进度
private int progress = 0;
/**
* 小圆点的当前进度
*/
public float mDotProgress;
// View宽
private int mWidth;
// View高
private int mHeight;
private int indexColor;
private int baseColor;
private int dotColor;
private int textSize;
private int textColor;
private ValueAnimator animator;
public CircleLoadingView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CircleLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CircleLoadingView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
// 获取用户配置属性
TypedArray tya = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CircleLoading);
baseColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_baseColor, Color.LTGRAY);
indexColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_indexColor, Color.BLUE);
textColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_textColor, Color.BLUE);
dotColor = tya.getColor(R.styleable.CircleLoading_dotColor, Color.RED);
textSize = tya.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CircleLoading_textSize, 36);
tya.recycle();
initUI();
}
private void initUI() {
mCOntext= getContext();
// 刻度画笔
mScalePaint = new Paint();
mScalePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mScalePaint.setStrokeWidth(DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 1));
mScalePaint.setStrokeCap(Paint.Cap.ROUND);
mScalePaint.setColor(baseColor);
mScalePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
// 小圆点画笔
mDotPaint = new Paint();
mDotPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mDotPaint.setColor(dotColor);
mDotPaint.setStrokeWidth(DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 1));
mDotPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
// 文字画笔
mTextPaint = new Paint();
mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mTextPaint.setColor(textColor);
mTextPaint.setTextSize(textSize);
mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth(DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 1));
mTextPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
drawArcScale(canvas);
drawTextValue(canvas);
drawRotateDot(canvas);
}
/**
* 画刻度
*/
private void drawArcScale(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
for (int i = 0; i <100; i++) {
if (progress > i) {
mScalePaint.setColor(indexColor);
} else {
mScalePaint.setColor(baseColor);
}
canvas.drawLine(mWidth / 2, 0, mHeight / 2, DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 10), mScalePaint);
// 旋转的度数 = 100 / 360
canvas.rotate(3.6f, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
}
canvas.restore();
}
/**
* 画内部数值
*/
private void drawTextValue(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
String showValue = String.valueOf(progress);
Rect textBound = new Rect();
mTextPaint.getTextBounds(showValue, 0, showValue.length(), textBound); // 获取文字的矩形范围
float textWidth = textBound.right - textBound.left; // 获得文字宽
float textHeight = textBound.bottom - textBound.top; // 获得文字高
canvas.drawText(showValue, mWidth / 2 - textWidth / 2, mHeight / 2 + textHeight / 2, mTextPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
/**
* 画旋转小圆点
*/
private void drawRotateDot(final Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
canvas.rotate(mDotProgress * 3.6f, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2);
canvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 10) + DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 5), DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 3), mDotPaint);
canvas.restore();
}
/**
* 启动小圆点旋转动画
*/
public void startDotAnimator() {
animator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 100);
animator.setDuration(1500);
animator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
animator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART);
animator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());
animator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
// 设置小圆点的进度,并通知界面重绘
mDotProgress = (Float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
animator.start();
}
/**
* 设置进度
*/
public void setProgress(int progress) {
this.progress = progress;
invalidate();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int myWidthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int myWidthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int myHeightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int myHeightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 获取宽
if (myWidthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// match_parent/精确值
mWidth = myWidthSpecSize;
} else {
// wrap_content
mWidth = DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 120);
}
// 获取高
if (myHeightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// match_parent/精确值
mHeight = myHeightSpecSize;
} else {
// wrap_content
mHeight = DensityUtil.dip2px(mContext, 120);
}
// 设置该view的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight);
}
}
总结
在的onDraw方法中需要避免频繁的new对象,所以把一些如初始化画笔Paint的方法放到了最前面的构造方法中进行。
在分多个模块绘制时,应该使用canvas.save()和canvas.restore()的组合,来避免不同模块绘制时的相互干扰,在这两个方法中绘制相当于PS中的图层概念,上一个图层进行的修改不会影响到下一个图层的显示效果。
在需要显示动画效果的地方使用属性动画来处理,可自定义的效果强,在系统提供的插值器类不够用的情况下,我么还可通过继承Animation类,重写它的applyTransformation方法来处理各种复杂的动画效果。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有