作者:王晓宁smile | 来源:互联网 | 2023-02-10 10:21
前言
打开手机游戏列表发现了一款经典的扫雷游戏,在玩的过程中发现游戏逻辑应该不难,想着是不是能自己写写这个游戏,后来用了1天实现了整体游戏开发,于是有了这篇文章来总结整体的游戏开发思路。
一、扫雷游戏规则是什么?
1、游戏为在10*10或其它排序组合网格中找雷
2、网格中隐藏着一定数量的雷,点击到雷即为输
3、点击无雷的网格会显示其临近8个方向上的总雷数,若为0则临近8个方向上的网格也会自动显示雷数,以此类推,直到出现不为0的网格
4、长按网格可以标记网格为雷
5、找出所有的雷即为胜利
二、开发前准备
1.创建小程序项目
使用微信开发者工具创建一个小程序项目。推荐使用官方推荐模板(此游戏项目使用js来实现)
2.开始开发
2.1.实现网格地图
页面初始数据:
groundSize: [16, 16], // 地图大小
minePosition: [], // 保存雷的位置
secondInterval: 0, // 时间定时器
data: {
second: 0, // 游戏时间
mineCount: 24, // 雷总数
markMineCount: 0, // 已标记雷数
renderGridList: [], // 网格列表
},此地图为16*16的地图,行列大小根据 groundSize 来,后续可以设置不同的地图大小。
地图wxml代码(具体样式自行规划):
renderGridList 渲染列表结构(二维数组):
[
[
{
isMine: false, // 是否为雷
mineTag: false, // 手动添加是否是雷的标识
isBoom: false, // 是否点击到了雷
mineNum: 0, // 周围雷数
showNum: false, // 是否显示雷数
value: 0, // 等同于id
position: [0, 0], // 标志在第几行第几列
},
...
],
...
]初始化网格方法:
initGrid() {
const gridList = [];
// 当前遍历gridList到第几个元素
let currentNum = 0;
// 当前遍历minePosition到第几个元素
let currentMineIndex = 0;
for (let i = 0; i 2.2.生成雷
generateMine() {
this.minePosition = [];
// 已设置的雷总数
let hadSetCount = 0;
// 随机最大值根据网格大小来
const groundCount = this.groundSize[0] * this.groundSize[1];
if (this.data.mineCount >= groundCount) {
return;
}
while (hadSetCount (a > b ? 1 : -1));
}根据页面初始数据中的 mineCount 来指定生成的雷数,通过随机值函数来生产随机的雷的 value 值,每生成一个先判断值是否在 minePosition 数组存在,不存在就push到 minePosition 数组中去。最终结果如下:在 initGrid 方法中会根据 minePosition 对应的值和网格的value值作比较,相等即为雷。
minePosition (24) [10, 17, 25, 28, 34, 35, 48, 73, 106, 132, 152, 187, 196, 197, 199, 203, 210, 217, 220, 226, 234, 238, 240, 245]
2.3.生成雷数
generateMineNum(gridList) {
gridList.forEach(row => {
row.forEach(col => {
// 是雷则跳过
if (col.isMine) {
return;
}
col.mineNum = this.checkMine(gridList, col.position);
});
});
return gridList;
},
checkMine(gridList, position) {
const [i, j] = position;
let mineNum = 0;
// 判断8个方位是否有雷
// 上 [i - 1][j]
if (gridList[i - 1] && gridList[i - 1][j].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 右上 [i - 1][j + 1]
if (gridList[i - 1] && gridList[i - 1][j + 1] && gridList[i - 1][j + 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 右 [i][j + 1]
if (gridList[i][j + 1] && gridList[i][j + 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 右下 [i + 1][j + 1]
if (gridList[i + 1] && gridList[i + 1][j + 1] && gridList[i + 1][j + 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 下 [i + 1][j]
if (gridList[i + 1] && gridList[i + 1][j].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 左下 [i + 1][j - 1]
if (gridList[i + 1] && gridList[i + 1][j - 1] && gridList[i + 1][j - 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 左 [i][j - 1]
if (gridList[i][j - 1] && gridList[i][j - 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
// 左上 [i - 1][j - 1]
if (gridList[i - 1] && gridList[i - 1][j - 1] && gridList[i - 1][j - 1].isMine) {
mineNum += 1;
}
return mineNum;
}判断8个方向上是否有雷时我们需要注意那些在边角的网格,这些网格方向少于8个,所以我们在做判断是需先判断其方向上是否有网格才行。
2.4.长按添加雷的标识
setMineTag(e) {
const {
currentTarget: {
dataset: { value },
},
} = e;
const renderGridList = this.data.renderGridList;
let markMineCount = 0;
for (const row of renderGridList) {
for (const col of row) {
if (col.value === value) {
col.mineTag = !col.mineTag;
}
if (col.mineTag) {
markMineCount += 1;
}
}
}
this.setData({
renderGridList,
markMineCount,
});
},我们在网格上设置 data-value ,这样长按事件就能获取对应的 value 值,通过遍历比较找到对应的网格并对网格的 mineTag 属性取反来达到长按标记或取消的功能,同时 mineTag 为真时需记录下标记数量。
2.5.点击网格事件
clearBox(e) {
const {
currentTarget: {
dataset: { value },
},
} = e;
let renderGridList = this.data.renderGridList;
out: for (const row of renderGridList) {
for (const col of row) {
if (col.value === value) {
// 判断是否是雷,为雷则输
col.isBoom = col.isMine;
if (col.isBoom) {
wx.showToast({
icon: 'error',
title: '踩到雷了',
});
break out;
}
renderGridList = this.loopClearBox(renderGridList, col);
break out;
}
}
}
this.setData({
renderGridList,
});
},
loopClearBox(gridList, col) {
if (col.isMine || col.showNum) {
return gridList;
}
col.showNum = true;
if (col.mineNum) {
return gridList;
}
// 判断相邻的4个方位是否为空并递归遍历
const [i, j] = col.position;
if (gridList[i - 1]) {
// 上
col = gridList[i - 1][j];
if (col) {
if (!col.mineNum) {
gridList = this.loopClearBox(gridList, col);
} else {
col.showNum = !col.isMine;
}
}
}
if (gridList[i + 1]) {
// 下
col = gridList[i + 1][j];
if (col) {
if (!col.mineNum) {
gridList = this.loopClearBox(gridList, col);
} else {
col.showNum = !col.isMine;
}
}
}
// 左
col = gridList[i][j - 1];
if (col) {
if (!col.mineNum) {
gridList = this.loopClearBox(gridList, col);
} else {
col.showNum = !col.isMine;
}
}
// 右
col = gridList[i][j + 1];
if (col) {
if (!col.mineNum) {
gridList = this.loopClearBox(gridList, col);
} else {
col.showNum = !col.isMine;
}
}
return gridList;
}loopClearBox 是递归遍历方法,当点击的网格的周围雷数为空时我们需要递归其上下左右方向的网格。效果如图所示:
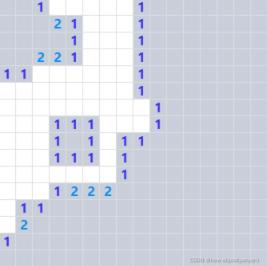
递归只有遇到有雷数的网格才会停下。
2.6.输赢判断
checkWin() {
// 当标记数小于总雷数时才判断输赢
if (this.data.mineCount >= this.data.markMineCount) {
// 遍历网格判断标记的雷是否正确
for (let row in this.data.renderGridList) {
for (let col of row) {
if (col.isMine !== col.mineTag) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}输赢判断是在点击网格事件中执行的,当返回值为true时即为通关。
总结
以上就是整个游戏开发的整体思路讲解,代码量不多,总体js代码只有2百多行,设计思路也比较简单。对于在开发中的收获,或许就是当你玩着自己开发的游戏时,作为程序员的快乐。
希望这篇文章对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。