3、解释部分C++代码
PyObject* pParams = Py_BuildValue("(ss)", "/oss/upload?bucket=test&filekey=test/image/3b/3ba9d94cab2f8868823d71c4445e125a.pngn" , "q4mJAS777BUbbdVpEqh2XRcZZqNyDweU4GRnM690");
在这里我输入了两个字符串类型的参数,Py_BuildValue()函数的作用和PyArg_ParseTuple()的作用相反,它将C类型的数据结构转换成Python对象。
该函数可以和PyArg_ParseTuple()函数一样识别一系列的格式串,但是输入参数只能是值,而不能是指针。
它返回一个Python对象和PyArg_ParseTuple()不同的一点是PyArg_ParseTuple()函数它的第一个参数为元组,Py_BuildValue()则不一定会生成一个元组。它生成一个元组仅仅当格式串包含两个或者多个格式单元,如果格式串为空,返回NONE。
在下面的描述中,括号中的项是格式单元返回的Python对象类型,方括号中的项为传递的C的值的类型。
“s” (string) [char *] :将C字符串转换成Python对象,如果C字符串为空,返回NONE。
“s#” (string) [char *, int] :将C字符串和它的长度转换成Python对象,如果C字符串为空指针,长度忽略,返回NONE。
“z” (string or None) [char *] :作用同”s”。
“z#” (string or None) [char *, int] :作用同”s#”。
“i” (integer) [int] :将一个C类型的int转换成Python int对象。
“b” (integer) [char] :作用同”i”。
“h” (integer) [short int] :作用同”i”。
“l” (integer) [long int] :将C类型的long转换成Pyhon中的int对象。
“c” (string of length 1) [char] :将C类型的char转换成长度为1的Python字符串对象。
“d” (float) [double] :将C类型的double转换成python中的浮点型对象。
“f” (float) [float] :作用同”d”。
“O&” (object) [converter, anything] :将任何数据类型通过转换函数转换成Python对象,这些数据作为转换函数的参数被调用并且返回一个新的Python对象,如果发生错误返回NULL。
“(items)” (tuple) [matching-items] :将一系列的C值转换成Python元组。
“[items]” (list) [matching-items] :将一系列的C值转换成Python列表。
“{items}” (dictionary) [matching-items] :将一系类的C值转换成Python的字典,每一对连续的C值将转换成一个键值对。
例如:
Py_BuildValue(“”) None
Py_BuildValue(“i”, 123) 123
Py_BuildValue(“iii”, 123, 456, 789) (123, 456, 789)
Py_BuildValue(“s”, “hello”) ‘hello’
Py_BuildValue(“ss”, “hello”, “world”) (‘hello’, ‘world’)
Py_BuildValue(“s#”, “hello”, 4) ‘hell’
Py_BuildValue(“()”) ()
Py_BuildValue(“(i)”, 123) (123,)
Py_BuildValue(“(ii)”, 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue(“(i,i)”, 123, 456) (123, 456)
Py_BuildValue(“[i,i]”, 123, 456) [123, 456] Py_BuildValue(“{s:i,s:i}”, “abc”, 123, “def”, 456) {‘abc’: 123, ‘def’: 456}
Py_BuildValue(“((ii)(ii)) (ii)”, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) (((1, 2), (3, 4)), (5, 6))
3、运行C++程序
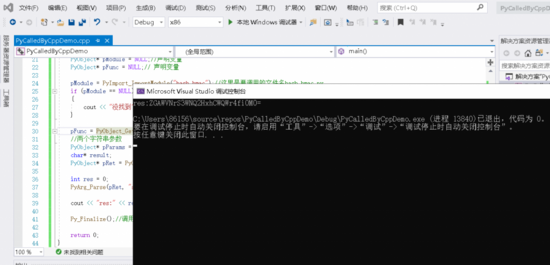
与Python代码的预期相同。
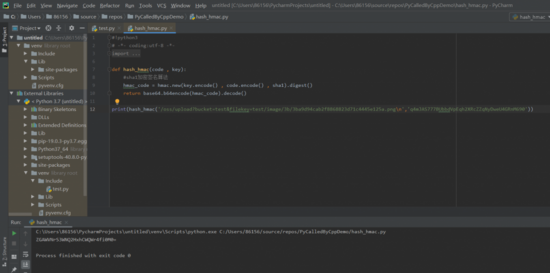
三、Python代码处理
在发布软件的时候,通常我们都不希望代码可以直接被别人看到。