最近学Socket学上瘾了,就写了一个简单的文件传输程序。
客户端设计思路:客户端与服务端建立连接,选择客户端本地文件,先将文件名及大小等属性发送给服务端,再将文件通过流的方式传输给服务端。传输的进度打印到控制台中,直到传输完成。
服务端设计思路:服务端接收客户端的请求(阻塞式),每接收到一个客户端请求连接后,就新开一个处理文件的线程,开始写入流,将文件到服务器的指定目录下,并与传输过来的文件同名。
下面是客户端和服务端的代码实现:
客户端代码:
import java.io.DataOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.net.Socket; /** * 文件传输Client端
* 功能说明: * * @author 大智若愚的小懂 * @Date 2016年09月01日 * @version 1.0 */ public class FileTransferClient extends Socket { private static final String SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1"; // 服务端IP private static final int SERVER_PORT = 8899; // 服务端端口 private Socket client; private FileInputStream fis; private DataOutputStream dos; /** * 构造函数
* 与服务器建立连接 * @throws Exception */ public FileTransferClient() throws Exception { super(SERVER_IP, SERVER_PORT); this.client = this; System.out.println("Cliect[port:" + client.getLocalPort() + "] 成功连接服务端"); } /** * 向服务端传输文件 * @throws Exception */ public void sendFile() throws Exception { try { File file = new File("E:\\JDK1.6中文参考手册(JDK_API_1_6_zh_CN).CHM"); if(file.exists()) { fis = new FileInputStream(file); dos = new DataOutputStream(client.getOutputStream()); // 文件名和长度 dos.writeUTF(file.getName()); dos.flush(); dos.writeLong(file.length()); dos.flush(); // 开始传输文件 System.out.println("======== 开始传输文件 ========"); byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length = 0; long progress = 0; while((length = fis.read(bytes, 0, bytes.length)) != -1) { dos.write(bytes, 0, length); dos.flush(); progress += length; System.out.print("| " + (100*progress/file.length()) + "% |"); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("======== 文件传输成功 ========"); } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(fis != null) fis.close(); if(dos != null) dos.close(); client.close(); } } /** * 入口 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileTransferClient client = new FileTransferClient(); // 启动客户端连接 client.sendFile(); // 传输文件 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
服务端代码:
import java.io.DataInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.math.RoundingMode; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.text.DecimalFormat; /** * 文件传输Server端
* 功能说明: * * @author 大智若愚的小懂 * @Date 2016年09月01日 * @version 1.0 */ public class FileTransferServer extends ServerSocket { private static final int SERVER_PORT = 8899; // 服务端端口 private static DecimalFormat df = null; static { // 设置数字格式,保留一位有效小数 df = new DecimalFormat("#0.0"); df.setRoundingMode(RoundingMode.HALF_UP); df.setMinimumFractionDigits(1); df.setMaximumFractionDigits(1); } public FileTransferServer() throws Exception { super(SERVER_PORT); } /** * 使用线程处理每个客户端传输的文件 * @throws Exception */ public void load() throws Exception { while (true) { // server尝试接收其他Socket的连接请求,server的accept方法是阻塞式的 Socket socket = this.accept(); /** * 我们的服务端处理客户端的连接请求是同步进行的, 每次接收到来自客户端的连接请求后, * 都要先跟当前的客户端通信完之后才能再处理下一个连接请求。 这在并发比较多的情况下会严重影响程序的性能, * 为此,我们可以把它改为如下这种异步处理与客户端通信的方式 */ // 每接收到一个Socket就建立一个新的线程来处理它 new Thread(new Task(socket)).start(); } } /** * 处理客户端传输过来的文件线程类 */ class Task implements Runnable { private Socket socket; private DataInputStream dis; private FileOutputStream fos; public Task(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } @Override public void run() { try { dis = new DataInputStream(socket.getInputStream()); // 文件名和长度 String fileName = dis.readUTF(); long fileLength = dis.readLong(); File directory = new File("D:\\FTCache"); if(!directory.exists()) { directory.mkdir(); } File file = new File(directory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separatorChar + fileName); fos = new FileOutputStream(file); // 开始接收文件 byte[] bytes = new byte[1024]; int length = 0; while((length = dis.read(bytes, 0, bytes.length)) != -1) { fos.write(bytes, 0, length); fos.flush(); } System.out.println("======== 文件接收成功 [File Name:" + fileName + "] [Size:" + getFormatFileSize(fileLength) + "] ========"); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { try { if(fos != null) fos.close(); if(dis != null) dis.close(); socket.close(); } catch (Exception e) {} } } } /** * 格式化文件大小 * @param length * @return */ private String getFormatFileSize(long length) { double size = ((double) length) / (1 <<30); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "GB"; } size = ((double) length) / (1 <<20); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "MB"; } size = ((double) length) / (1 <<10); if(size >= 1) { return df.format(size) + "KB"; } return length + "B"; } /** * 入口 * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { try { FileTransferServer server = new FileTransferServer(); // 启动服务端 server.load(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
测试的结果(客户端):
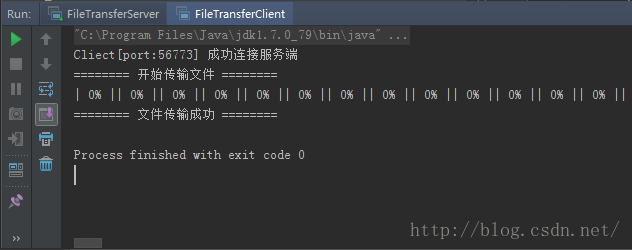
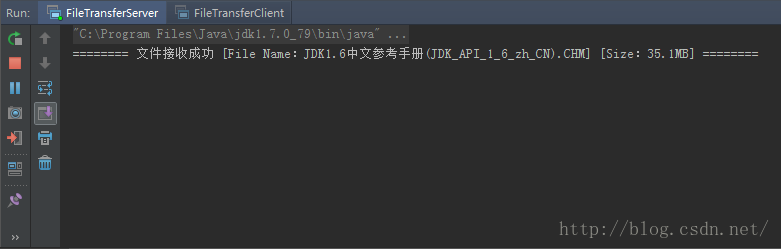
测试的结果(服务端):
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有