前言
Android底层服务,即运行在 linux 下的进程,是 Android 系统运行的基础,完成 Android 或者说计算机最基本的功能。比如连接服务(包括 WIFI,BT 等等);比如 Android 的 adb 功能;比如存储监控等等。没有这些底层服务,上层也就没有了对应的功能。
Android 底层服务往往是常驻内存,时刻运行完成任务。底层服务进程,往往具有更多的权限,可能和驱动通信,可能和 linux 内核通信,可能需要操作系统核心运行文件以及节点等等。所以,底层服务,可以帮你完成更多计算机基本功能。
本文所使用的 AOSP 是基于 Android 8.1。阅读文本需要对 Android 的架构、编译系统、AOSP工程和 SeAndroid 有基本认识。
创建守护进程
创建目录编写代码
创建目录
我们在 Android 系统通用守护进程目录下创建我们的守护进程,当然你也可以在其它目录下放置你的守护进程。
/system/core/
在上面的目录下,创建守护进程的文件夹 nativeservice,那么,我们的守护进程就存在如下目录,下文中称简称目录代表如下目录。
/system/core/nativeservice/
编写代码
在目录中创建主代码文件 native_main.cpp。另外,我们需要编译,那么就需要 mk 文件,创建一个 Android.mk 文件。这时,目录架构就是如下这个样子
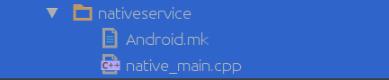
编写Android.mk
我在代码中尽可能的注释清楚重要语句的作用,读者如果对 Android AOSP 编译不了解的,可以查阅更多 mk 语法的资料学习。
# Copyright 2013 The Android Open Source Project # 当前路径 LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) #清除历史变量 include $(CLEAR_VARS) ### nativeservice ### #待编译的源码文件 LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \ native_main.cpp \ common_c_includes := \ bionic \ system/core/include/sysutils \ #引用一些函数库 common_shared_libraries := \ libsysutils \ libcutils \ liblog \ libutils \ libbinder \ libbase LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := \ $(common_c_includes) #守护进程的名字 LOCAL_MODULE := nativeservice LOCAL_CFLAGS := -Wall -Wno-unused-parameter -Werror LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES := \ $(common_shared_libraries) LOCAL_MODULE_TAGS := optional #编译守护进程,也就是可执行文件 #编译后,在/system/bin/ 下,变多了 nativeservice 可执行文件。 include $(BUILD_EXECUTABLE)
编写native_main.cpp
在 Linux 中,一个开机启动的服务,执行完后会自动退出,而我们是守护进程,那么就需要一直运行。让程序一直运行有很多种方法。在 native_main.cpp 中贴出了三种方式,它们分别是 epoll,有名管道(FIFO)和循环。
epoll 的方式是 Android 系统比较常见的方式,系统的电池状态变化、USB 接口状态变化等守护进程便是通过 epoll 的方式,实时鉴定并读取新状态。
有名管道,在 IPC 通信中比较简单、便捷,适合轻量级任务。
循环,这个是最老套的方式。
三种方式在 native_main.cpp 都贴出来了,本文侧重使用有名管道(FIFO)的方式,鉴于篇幅过长,其它方式就一笔带过了,如果读者对 epoll 等较为兴趣的,可以自行查阅更多资料学习。
下面是 native_main.cpp 的代码,请认真看注释哦。
// // Created familyyuan user on 18-4-20. // #include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #include #define MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS 40 //epoll方式的 epoll fd static int epollfd; //FIFO 方式的 fd static int fifo_fd; //epoll方式的 uevent fd static int uevent_fd; #define BUFFER_SIZE PIPE_BUF int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { SLOGD("native_service start"); // // 1、epoll 的方式, // 监听一个 socket,如果 socket 被连接,便激活程序读取数据。 // Android 驱动和用户态程序较多使用这种方式交互。 // /* int eventct = 5; struct epoll_event events[eventct]; struct epoll_event ev; uevent_fd = uevent_open_socket(64*1024, true); //创建 epoll 通道,监听 socket fd epollfd = epoll_create(MAX_EPOLL_EVENTS); if (epollfd == -1) { SLOGD("native_service epoll_create failed"); } else { SLOGD("native_service epoll_create success"); } // fcntl(uevent_fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK); ev.events = EPOLLIN; ev.data.fd=uevent_fd; //注册 epoll fd if (epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, uevent_fd, &ev) == -1) { SLOGD("native_service epoll_ctl failed"); } else { SLOGD("native_service epoll_ctl success"); } while(1){ SLOGD("native_service epoll running"); int nevents = 0; // 监听 socket 端口 nevents = epoll_wait(epollfd, events, eventct, 100000); if (nevents == -1 || nevents == 0) { SLOGD("native_service epoll_wait failed"); } else { SLOGD("native_service epoll_wait success"); } epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, uevent_fd, &ev); } close(uevent_fd); */ // // 2、 FIFO 的方式, // 在/mnt/下创建一个名为 nativeservice 的管道, // 监听管道的数据变化,如果有数据写入管道,便读取数据。 // int res; int bytes = 0; char buffer[BUFFER_SIZE + 1]; // 创建 FIFO res = mkfifo("/mnt/nativeservice", 0777); if (res != 0){ SLOGD("native_service create fifo exist or failed"); } else{ SLOGD("native_service create fifo success"); } // 以阻塞的方式打开 FIFO,知道管道有数据写入,激活程序,往下执行 fifo_fd = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open("/mnt/nativeservice",O_RDONLY)); if (fifo_fd <0) { SLOGD("native_service open failed"); } else { SLOGD("native_service open success"); } if (fifo_fd != -1){ while(1){ //读取管道数据,如果没有数据,阻塞等待数据被写入,激活 res = read(fifo_fd, buffer, BUFFER_SIZE); bytes += res; SLOGD("native_service result=%s", buffer); } } else { SLOGD("native_service open failed"); } //关闭管道资源。 close(fifo_fd); // // 3、循环的方式 // 这种方式代码最简单,但是耗资源,没有实时性。 // 一个死循环,每隔 5 秒运行一次 // /* while(1){ SLOGD("native_service runnig"); sleep(5); SLOGD("native_service wake"); } */ SLOGD("native_service die"); return 0; }
推进编译系统
编写好 Android.mk 和 native_main.cpp 后,可以通过单边命令 “mmm system/core/nativeservice” 编译我们的守护进程了。但是此时用 make 编译整个 AOSP 时,却不会编译我们的 nativeservice。因此,需要告诉编译系统,编译工程时,同时编译 nativeservice。修改如下
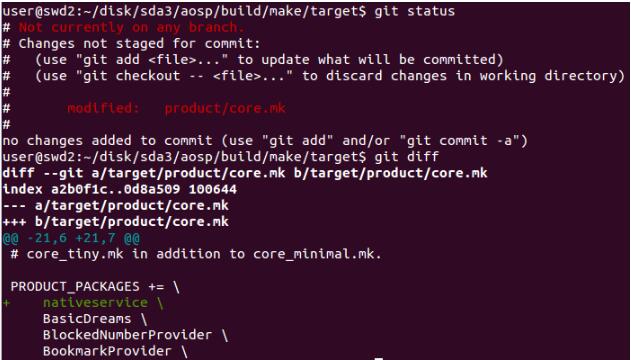
在 /build/make/target/product/core.mk 文件添加 nativeservice,当然不限制添加在这个文件,很多厂商的工程,也会增加自己的 PRODUCT_PACKAGES 配置 mk 文件。
配置开机启动
至此,编译整个工程,守护进程也可以被编译了,这个时候,刷到手机是否就可以运行了呢?不会的,我们还需要让守护进程在手机开机的时候运行起来,且运行中进程死掉的话,也需要重新启动守护进程。方法如下
在 system/core/rootdir/init.rc 文件中添加如下代码
service healthd /system/bin/healthd class core critical group root system wakelock #我们的代码开始 service nativeservice /system/bin/nativeservice class main #main类,属于main的服务会开机被运行,且死掉会重启 group system #属于 system 组 #user system #以system用户启动,不设置以root用户启动 seclabel u:r:nativeservice:s0 #SeAndroid SContext,domain是nativeservice restorecon nativeservice #我们的代码结束 service console /system/bin/sh
读者可以查看 AOSP 中 system/core/init/README.md 文件了解 init.rc 的语法和配置方法。对于 class core 等不同类别的区别,读者可以阅读《Android加密之全盘加密》相关的阐述。
配置SeAndroid
至此,编译整个工程,守护进程也可以被编译了,也配置了开机自启动。这个时候,刷到手机是否就可以运行守护进程了呢?不可以,我们知道 Android 继用了 SeLinux 安全机制,同时发展出 SeAndroid 机制,所有文件和进程都需要配置 SeAndroid 才能有权限。因此,如果没有给守护进程以及守护进程需要操作的目录和文件赋予权限,都会被 SeAndroid 过滤或禁止。
由于 QCOM 和 Mediatek 的不同,在相关文件的放置路径会不同,但是方法都是一样的,不同的平台,找到对应的路径下的文件就可以了。本文以 MTK 平台的为例。
1、在 device/mediatek/sepolicy/basic/non_plat/file_contexts 中添加如下代码
/system/bin/nativeservice u:object_r:nativeservice_exec:s0
2、在 device/mediatek/sepolicy/basic/non_plat/ 中添加 nativeservice.te 文件,文件内容如下
#守护进程 domain 为 nativeservice
type nativeservice, domain;
typeattribute nativeservice coredomain;
type nativeservice_exec, exec_type, file_type;
init_daemon_domain(nativeservice)
#allow nativeservice self:netlink_kobject_uevent_socket create_socket_perms_no_ioctl;
#allow nativeservice tmpfs:file { getattr open read write ioctl create };
#允许 nativeservice 在mnt目录读写管道文件
allow nativeservice tmpfs:fifo_file rw_file_perms;
#允许 nativeservice 在mnt目录创建管道文件
allow nativeservice tmpfs:fifo_file create_file_perms;
#允许 nativeservice 在mnt目录读写
allow nativeservice tmpfs:dir rw_dir_perms;
#允许 nativeservice 在mnt目录创建目录
allow nativeservice tmpfs:dir create_dir_perms;
刷机验证
至此,需要编译整个 AOSP 工程,当然,如果有编译过,只需要增量编译即可,很快就可以编译完成。
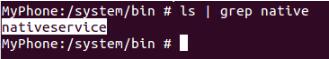
1、刷机后在手机的 /system/bin/nativeservie 目录下能看到守护进程;
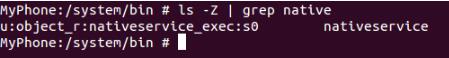
2、看一下 SeAndroid 的 SContext
3、看一下 FIFO 管道文件

4、prwx 前面的 p 代表是一个管道文件

5、管道文件 SeAndroid 的 tcontext
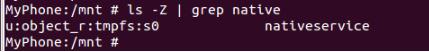
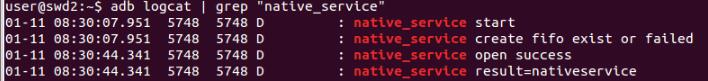
6、守护进程启动,启动后打开管道,等待管道数据写入。由于守护进程比抓 log 的工具启动还早,因此,开机时前面的 log 无法抓取,如下 log 是手动 kill 掉守护进程打印的 log

7、通过终端给管道写入数据

8、守护进程激活,读取数据
总结
Android 守护进程可以做很多上层无法完成的功能,但是,为了安全,要运用好 SeAndroid,以最小能力的原则去配置安全权限。创建守护进程,要编写对应代码,配置 rc 文件,配置 SeAndroid。
以上这篇创建Android守护进程实例(底层服务)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持。

 京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有
京公网安备 11010802041100号 | 京ICP备19059560号-4 | PHP1.CN 第一PHP社区 版权所有